
Security News
Research
Data Theft Repackaged: A Case Study in Malicious Wrapper Packages on npm
The Socket Research Team breaks down a malicious wrapper package that uses obfuscation to harvest credentials and exfiltrate sensitive data.
@transifex/native
Advanced tools
Transifex Native is a full end-to-end, cloud-based localization stack for moderns apps.
A general purpose Javascript library for localizing web apps using Transifex Native.
Requires a Transifex Native Project Token.
Supported Node.js versions >= 14.x.x
Related packages:
Learn more about Transifex Native in the Transifex Developer Hub.
Step1: Create a Transifex Native project in Transifex.
Step2: Grab credentials.
Step3: Internationalize the code using the SDK.
Step4: Push source phrases using the @transifex/cli tool.
Step5: Translate the app using over-the-air updates.
No translation files required.
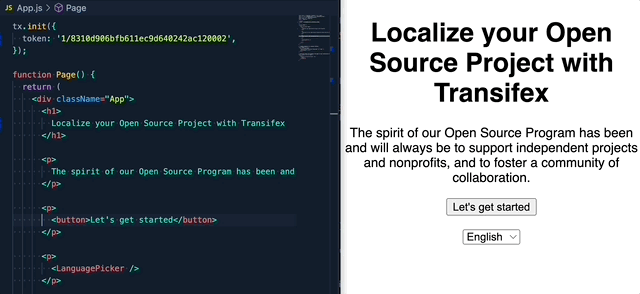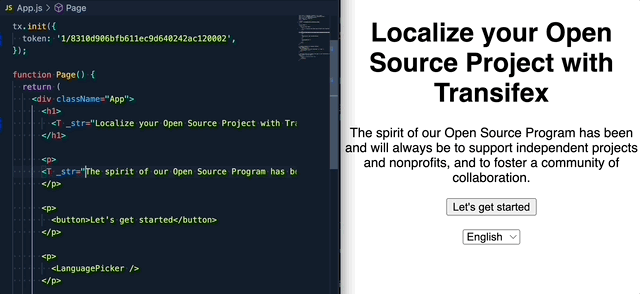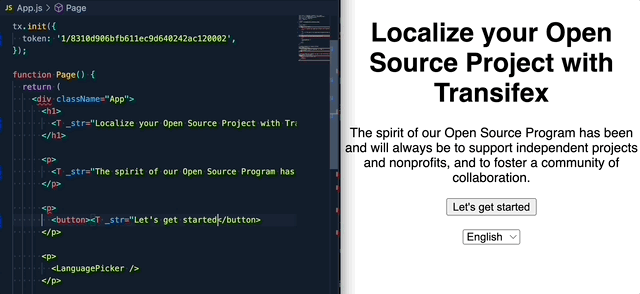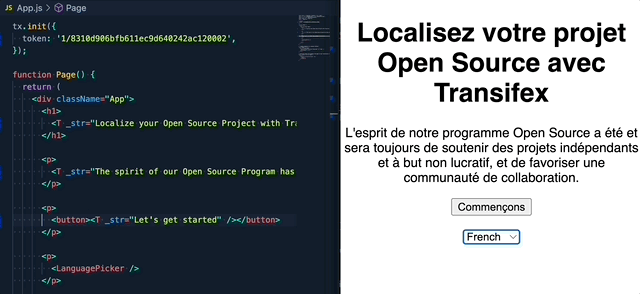
If you are upgrading from the 1.x.x version, please read this migration guide, as there are breaking changes in place.
Install the library using:
npm install @transifex/native --save
import { tx, t } from '@transifex/native';
// initialize
tx.init({
token: '<PUBLIC PROJECT TOKEN>',
});
async function main() {
// set target language, this will fetch translations Over The Air
await tx.setCurrentLocale('el');
// translate something
const message = t('Welcome {user}', {user: 'Joe'});
console.log(message);
// get supported languages in order to create a language picker
const languages = await tx.getLanguages();
console.log(languages);
/*
[{
name: 'Greek',
code: 'el',
localized_name: 'Ελληνικά',
rtl: false,
},{
...
}]
*/
}
main();
const { tx, t } = require('@transifex/native');
// initialize
tx.init({
token: '<PUBLIC PROJECT TOKEN>',
});
...
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@transifex/native/dist/browser.native.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
const tx = Transifex.tx;
const t = Transifex.t;
// initialize SDK
tx.init({
token: '<PUBLIC PROJECT TOKEN>',
});
// get all languages
tx.setCurrentLocale('fr').then(function() {
// translate something
const message = t('Welcome {user}', {user: 'Joe'});
console.log(message);
});
</script>
tx.init({
// Public project token, defaults to empty string
token: String,
// CDS endpoint, defaults to https://cds.svc.transifex.net
cdsHost: String,
// Fetch only strings that contain specific tags from CDS, e.g. "master,react"
filterTags: String,
// Fetch only strings matching translation status: reviewed,proofread,finalized
filterStatus: String,
// Missing translation policy, defaults to "new SourceStringPolicy()"
missingPolicy: Function,
// Error policy, defaults to "new SourceErrorPolicy()"
errorPolicy: Function,
// String renderer, defaults to "new MessageFormatRenderer()"
stringRenderer: Function,
// Translation cache, defaults to "new MemoryCache()"
cache: Function,
// Optional timeout in milliseconds when fetching languages and
// strings, defaults to 0 (no-timeout)
fetchTimeout: Number,
// Optional interval polling delay in milliseconds while waiting
// for CDS to warm-up with content, defaults to 250msec
fetchInterval: Number,
})
Fetches list of project languages from CDS, useful for creating a language picker.
tx.getLanguages(): Promise([
{
name: String,
code: String,
localized_name: String,
rtl: Boolean
},
...
])
// Example
tx.getLanguages().
then(languages => console.log(languages)).
catch(err => console.log(err))
Get a list of available locales based on CDS.
tx.getLocales(): Promise(['code', 'code',...])
Fetches translations from the CDS and stores them in cache. When the promise returns, all content will be translated to that language.
tx.setCurrentLocale(localeCode): Promise
// Example
tx.setCurrentLocale('el').
then(() => console.log('content loaded')).
catch(err => console.log(err))
Returns the currently selected language code.
tx.getCurrentLocale(): String(localeCode)
// Example
console.log(tx.getCurrentLocale())
Returns the translation of the passed source string based on the currenly selected language. If the translation is not found, the returned string is handled by the configured missing policy. If an error occurs in the ICU parsing of the string, the error is handled based on the configured error policy.
The translation is returned unescaped and it is NOT safe to be used inside the HTML document unless escaped
t(sourceString, params): String(localizedString)
sourceString: String(ICU syntax string)
params: Object({
// optional string context, affects key generation
_context: String,
// optional developer comment
_comment: String,
// optional character limit instruction for translators
_charlimit: Number,
// optional comma separated list of tags
_tags: String,
// optional custom key
_key: String,
// optionally escape ICU variables
_escapeVars: Boolean,
// ICU variables, plurals, gender etc
...icu variables...
})
// Example
console.log(
t('Hello <b>{username}</b>', { username: 'Joe' })
)
// "Hello <b>Joe</b>"
Using the translation as is from the t function inside HTML is dangerous for
XSS attacks. The translation must be escaped based on two scenarios.
import { t, escape } from '@transifex/native';
const translation = escape(t('Hello {username}', { username }));
// translation is safe to include in HTML
HTML source content cannot be globally escaped. In that case, we can just escape
the ICU variables using the _escapeVars parameter.
import { t } from '@transifex/native';
const html = t('<b>Hello {username}</b>', {
username: username,
_escapeVars: true,
});
For server side integrations you can also push source content programmatically without using the CLI.
tx.pushSource(payload, params): Promise
payload: Object({
key: {
string: String,
meta: {
context: String,
developer_comment: String,
character_limit: Number,
tags: Array(String),
occurrences: Array(String),
},
},
key: { .. }
})
params: Object({
// Replace the entire resource content with the pushed content of this request
purge: Boolean,
// Replace the existing string tags with the tags of this request
overrideTags: Boolean,
// If true, when wait for processing to be complete before
// resolving this promise
noWait: Boolean,
})
For example:
const { createNativeInstance } = require('@transifex/native');
const tx = createNativeInstance({
token: 'token',
secret: 'secret',
});
await tx.pushSource({
'mykey': {
string: 'My string',
meta: {
context: 'content', // optional
developer_comment: 'developer comment', // optional
character_limit: 10, // optional
tags: ['tag1', 'tag2'], // optional
occurrences: ['file.jsx', 'file2.js'], // optional
},
}
});
Server side integrations can also invalidate the CDS cache programmatically.
tx.invalidateCDS({
// if true, then purge the cache entirely (not recommended)
purge: Boolean,
}): Promise
For example:
const { createNativeInstance } = require('@transifex/native');
const tx = createNativeInstance({
token: 'token',
secret: 'secret',
});
await tx.invalidateCDS();
Library for listening to various async events.
// listen to event
onEvent(type, function)
type:
FETCHING_TRANSLATIONS
TRANSLATIONS_FETCHED
TRANSLATIONS_FETCH_FAILED
LOCALE_CHANGED
FETCHING_LOCALES
LOCALES_FETCHED
LOCALES_FETCH_FAILED
// stop listening event
offEvent(type, function)
// trigger an event
sendEvent(type, payload, caller)
const { tx, t, createNativeInstance } = require('@transifex/native');
// Initiatate a secondary TX Instance
const txOtherInstance = createNativeInstance();
txOtherInstance.init({
token: '<PUBLIC PROJECT TOKEN 2>',
})
// initialize SDK
tx.init({
token: '<PUBLIC PROJECT TOKEN>',
});
// Use tx as a controller of the other instance
tx.controllerOf(txOtherInstance);
// get all languages
tx.setCurrentLocale('fr').then(function() {
// translate something
const message = t('Welcome {user}', {user: 'Joe'});
console.log(message);
const message2 = txOtherInstance.t('Welcome {user}', {user: 'Joe'});
console.log(message2);
});
Licensed under Apache License 2.0, see LICENSE file.
FAQs
i18n framework using Transifex Native
We found that @transifex/native demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Research
The Socket Research Team breaks down a malicious wrapper package that uses obfuscation to harvest credentials and exfiltrate sensitive data.

Research
Security News
Attackers used a malicious npm package typosquatting a popular ESLint plugin to steal sensitive data, execute commands, and exploit developer systems.

Security News
The Ultralytics' PyPI Package was compromised four times in one weekend through GitHub Actions cache poisoning and failure to rotate previously compromised API tokens.