
Add this package to localize your React, React Native or JavaScript application.
Use this <Trans>React syntax</Trans>
or this t`JavaScript syntax` .
Write only the source text, and keep it synchronized with your translators on
Translation.io.
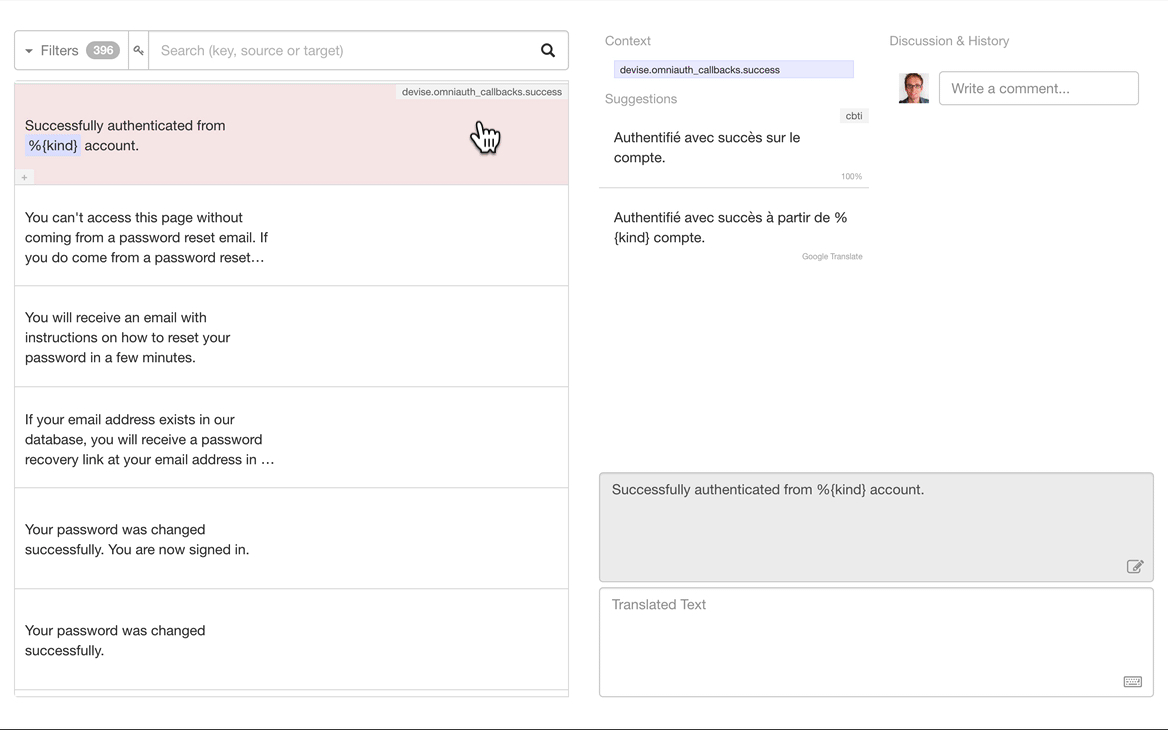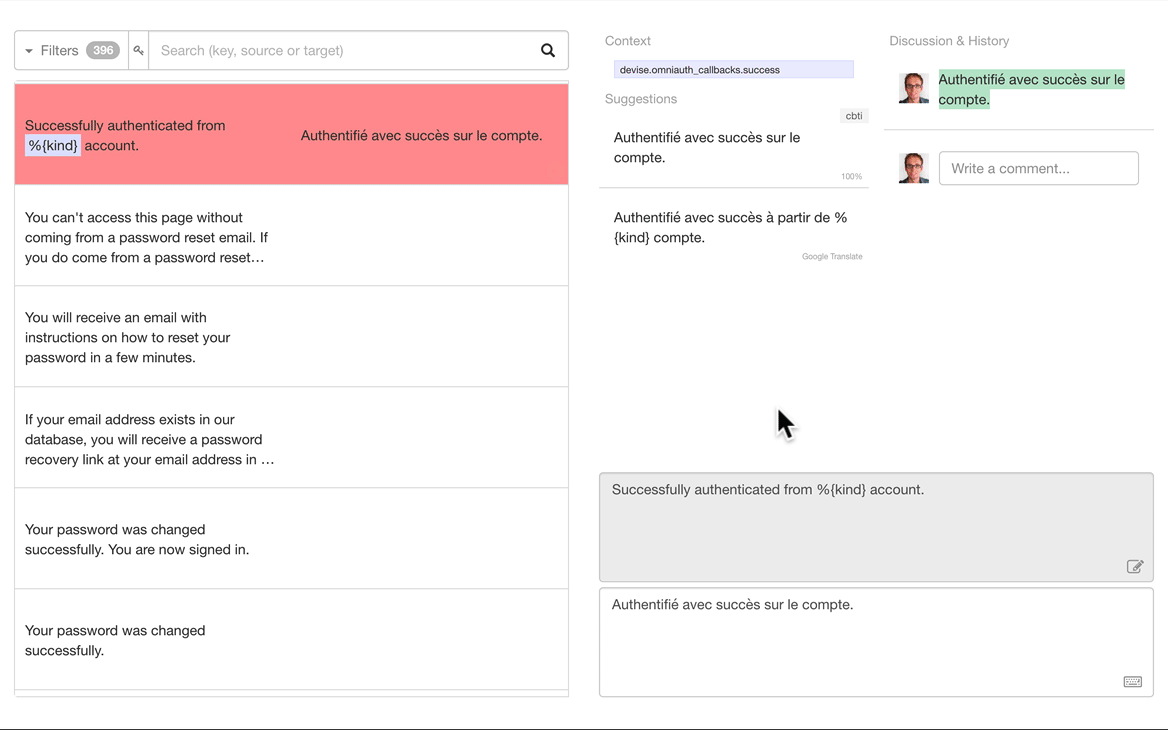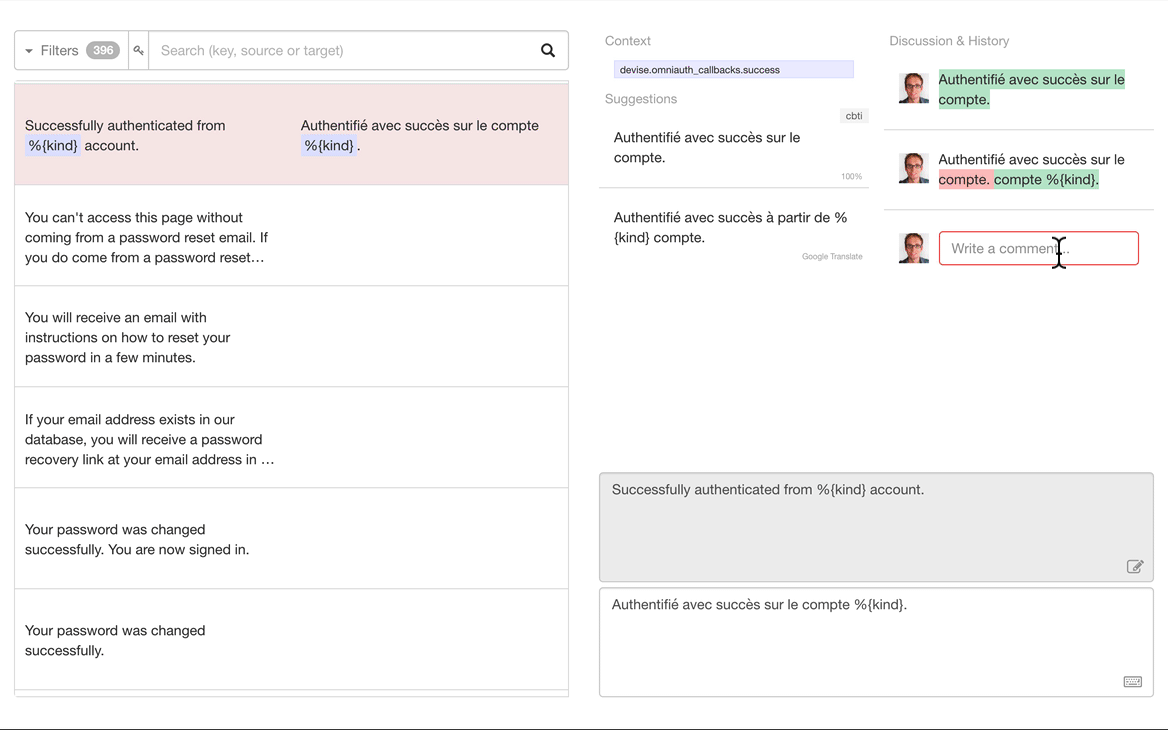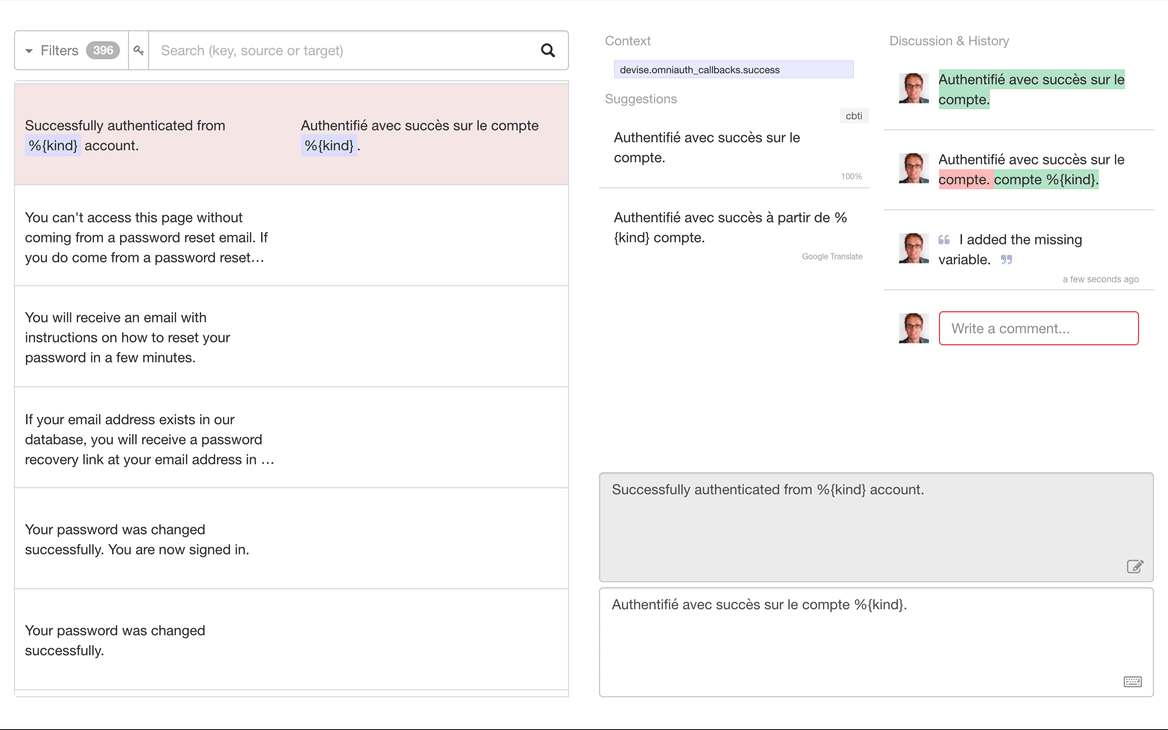
Important Information:
-
The Translation.io client is directly integrated into
the Lingui i18n framework.
-
This repository provides additional documentation and a useful meta-package
to simplify the installation of Lingui.
You can refer directly to the Lingui documentation for more advanced Lingui features.
- To use Lingui v5, you need to install
@translation/lingui v 3.0.0 (latest) - To use Lingui v4, you need to install
@translation/lingui v 2.0.0
Need help? contact@translation.io
Table of contents
Localization syntaxes
React JSX Syntax
Singular
import { Trans } from "@lingui/react/macro"
{}
<Trans>
Text to be translated
</Trans>
{}
<Trans>
Hello {name}
</Trans>
{}
<Trans comment="Acronym for Key Performance Indicator">
View KPIs
</Trans>
{}
<Trans>
Text with <em>HTML</em> tags
</Trans>
{}
<Trans>
Text with a
<a href="https://google.com" target="_blank">link</a>
</Trans>
{}
<div>
<Trans context="romantic meeting with someone">
Date
</Trans>
<Trans context="a moment in time">
Date
</Trans>
</div>
{}
<div>
<Trans id="index.header.title">
Dashboard
</Trans>
<Trans id="modal.buttons.cancel">
Cancel
</Trans>
</div>
N.B. Attributes (comment, context, id) can be used together.
Plural
import { Plural } from "@lingui/react/macro"
{}
<Plural
value={count}
one="You've got 1 message"
other="You've got # messages"
/>
{}
<Plural
value={count}
_0="Your inbox is empty!"
_42="You've found the ultimate answer"
one="You've got 1 message"
other="You've got # messages"
/>
{}
<Plural
value={count}
one={`Hello ${name}, you've got 1 message`}
other={`Hello ${name}, you've got # messages`}
/>
{}
<Plural
value={count}
one={<Trans>You've got <strong>1</strong> message</Trans>}
other={<Trans>You've got <strong>#</strong> messages</Trans>}
/>
Note: English has only 2 plural forms (one and other), but other languages
have more of them, from this list: zero, one, two, few, many,
other.
On Translation.io, your translators will see the correct list of plural forms directly
in the interface, with examples in their target language:
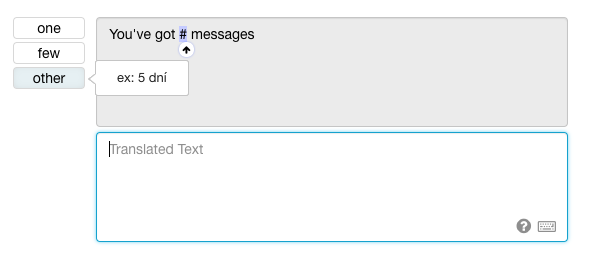
You can find the complete list of plural forms and plural rules here:
available languages and plural forms
JavaScript Syntax
Singular
import { t } from "@lingui/core/macro"
t`Text to be translated`
t`Hello ${name}`
t({
comment: "Acronym for Key Performance Indicator",
message: "View KPIs"
})
{}
t({
context: "romantic meeting with someone",
message: "Date"
})
t({
context: "a moment in time",
message: "Date"
})
{}
t({
id: "index.header.title",
message: "Dashboard"
})
t({
id: "modal.buttons.cancel",
message: "Cancel"
})
Plural
import { plural } from "@lingui/core/macro"
plural(count, {
one: "You've got 1 message",
other: "You've got # messages"
})
plural(count, {
_0: "Your inbox is empty!",
_42: "You've found the ultimate answer",
one: "You've got 1 message",
other: "You've got # messages"
})
plural(count, {
one: `Hello ${name}, you've got 1 message`,
other: `Hello ${name}, you've got # messages`
})
Note: English has only 2 plural forms (one and other) but other languages
have more of them, from this list: zero, one, two, few, many,
other.
Translators will have the correct list of plural forms proposed directly
in the interface, with examples in their target language:

You can find the complete list of plural forms and plural rules here:
https://translation.io/docs/languages_with_plural_cases
Installation
1. Install the package
Solution 1: Meta-package
Quick way to install Lingui with the correct dependencies.
npm install @translation/lingui
yarn add @translation/lingui
Solution 2: Fine-Grained Install
More complex but cleaner install, with some packages in development only.
npm install --save-dev @lingui/cli
npm install --save-dev @lingui/babel-plugin-lingui-macro
npm install @lingui/react
yarn add --dev @lingui/cli
yarn add --dev @lingui/babel-plugin-lingui-macro
yarn add @lingui/react
2. Add the following scripts
Add these lines to your package.json to make your life easier.
{
"scripts": {
"sync": "lingui extract --overwrite && lingui compile",
"sync_and_purge": "lingui extract --overwrite --clean && lingui compile"
}
}
3. Create a new translation project
Create your new project from the UI and select
the correct source and target languages.
4. Configure your project
Copy the .linguirc configuration file that was generated for you to the
root of your application.
The configuration file looks like this:
{
"locales": ["en", "fr", "nl", "de", "es"],
"sourceLocale": "en",
"catalogs": [{
"path": "src/locales/{locale}/messages",
"include": ["src"]
}],
"format": "po",
"service": {
"name": "TranslationIO",
"apiKey": "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz012345"
}
}
5. Setup your application
For React (cf. React Documentation or React Native documentation):
import { i18n } from '@lingui/core'
import { I18nProvider } from '@lingui/react'
import { messages } from './locales/en/messages'
import Inbox from './Inbox'
i18n.load('en', messages)
i18n.activate('en')
const App = () => (
<I18nProvider i18n={i18n}>
<Inbox />
</I18nProvider>
)
For JavaScript (cf. documentation):
import { i18n } from '@lingui/core'
import { messages } from './locales/en/messages'
i18n.load('en', messages)
i18n.activate('en')
6. Localize your code
Localize your app using the <Trans>React syntax</Trans>
or the t`JavaScript syntax` .
7. Initialize your project
Run the following commands to push your source keys and
existing translations to Translation.io:
npm run sync
yarn sync
If you need to add or remove languages in the future, please read
this section about that.
Usage
Sync
To send new translatable strings and get new translations from Translation.io,
and at the same time generate the minified Javascript catalog files, simply run:
npm run sync
yarn sync
Sync and Purge
If you need to remove unused strings from Translation.io, using
the current branch as reference, use the --clean option.
npm run sync_and_purge
yarn sync_and_purge
As the name says, this operation will also perform a sync at the same time.
Warning: all strings that are not present in the current local branch will be
permanently deleted from Translation.io.
Manage Languages
Add or Remove Language
You can add or remove a language by updating "locales": [] in your
.linguirc file, and syncing your project again.
If you want to add a new language with existing translations (ex. if you already have
a translated PO file in your project), you will need to create a
new empty project on Translation.io and init it for the first time again.
Edit Language
To edit existing languages while keeping their translations (e.g. changing from en to en-US).
- Create a new project on Translation.io with the correct languages.
- Adapt
.linguirc (new API key and languages) - Adapt the language code in the PO directory structure, and also the language header in PO files.
- Sync your project for the first time and check that everything went fine.
- Invite your collaborators in the new project.
- Remove the old project.
Since you created a new project, the translation history and tags will unfortunately be lost.
Custom Languages
Custom languages are convenient if you want to customize translations for a specific customer
or another instance of your application.
A custom language is always be derived from an existing language.
Its structure should be like:
`${existingLanguageCode}-${customText}`
where customText can only contain alphabetic characters and -.
Examples: en-microsoft or fr-BE-custom.
Fallbacks
Language fallbacks will work as expected for any regional or custom
language. It means that if the en-GB translation is missing,
then it will fallback to en. So you only need to translate keys that
are different from the main language when you specialize a language.
Note that fallbacks are chained, so en-US-custom will fallback to en-US that will
fallback to en.
You can find more information about Lingui fallback configuration
here.
Change the current locale
You can change the current locale by using:
import { i18n } from '@lingui/core'
import { messages } from './locales/en/messages.js'
i18n.load('en', messages)
i18n.activate('en')
You may be able to detect the default locale of the user, based on many things
like navigator meta tags, HTML language tag, subdomain, path, cookie, etc.
The easiest way to do that would be to use the small
@lingui/detect-locale package.
import { detect, fromUrl, fromStorage, fromNavigator } from "@lingui/detect-locale"
const DEFAULT_FALLBACK = () => "en"
const result = detect(
fromUrl("lang"),
fromStorage("lang"),
fromNavigator(),
DEFAULT_FALLBACK
)
console.log(result)
You will find more information about this package
here
Dynamic loading of .JS translation catalogs
It’s your responsibility to load the correct translation catalog based on the active locale.
There is a clean dynamic loader helper
that will assist you with this task.
import { i18n } from '@lingui/core';
export const locales = {
en: "English",
cs: "Česky",
};
export const defaultLocale = "en";
export async function dynamicActivate(locale: string) {
const { messages } = await import(`./locales/${locale}/messages`)
i18n.load(locale, messages)
i18n.activate(locale)
}
Please read more about this loader here.
List of clients for Translation.io
The following clients are officially supported by Translation.io
and are well documented.
Some of these implementations (and other non-officially supported ones)
were started by contributors for their own translation projects.
We are thankful to all contributors for their hard work!
Ruby on Rails (Ruby)
Officially supported on https://translation.io/rails
Credits: @aurels, @michaelhoste
Laravel (PHP)
Officially supported on https://translation.io/laravel
Credits: @armandsar, @michaelhoste
React, React Native and JavaScript
Officially supported on https://translation.io/lingui
Translation.io is directly integrated in the great
Lingui internationalization project.
Angular
Officially supported on https://translation.io/angular
Credits: @SimonCorellia, @didier-84, @michaelhoste
Others
If you want to create a new client for your favorite language or framework, please read our
Create a Translation.io Library
guide and use the special
init and
sync endpoints.
You can also use the more traditional API.
Feel free to contact us on contact@translation.io
if you need some help or if you want to share your library.
Contributing
This is a dumb meta-package that doesn't need any contribution.
If you want to contribute, please refer to
the official Lingui CONTRIBUTING.md
file.
License
This meta-package is released under MIT license.
The Lingui MIT License is located here here
(c) https://translation.io / contact@translation.io






