
Security News
Deno 2.2 Improves Dependency Management and Expands Node.js Compatibility
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.
@xenova/transformers
Advanced tools
Run 🤗 Transformers in your browser! We currently support BERT, ALBERT, DistilBERT, MobileBERT, SqueezeBERT, T5, T5v1.1, FLAN-T5, mT5, BART, MarianMT, GPT2, GPT Neo, CodeGen, Whisper, CLIP, Vision Transformer, VisionEncoderDecoder, and DETR models, for a
Run 🤗 Transformers in your browser! We currently support BERT, ALBERT, DistilBERT, MobileBERT, SqueezeBERT, T5, T5v1.1, FLAN-T5, mT5, BART, MarianMT, GPT2, GPT Neo, CodeGen, Whisper, CLIP, Vision Transformer, VisionEncoderDecoder, and DETR models, for a variety of tasks including: masked language modelling, text classification, token classification, zero-shot classification, text-to-text generation, translation, summarization, question answering, text generation, automatic speech recognition, image classification, zero-shot image classification, image-to-text, and object detection.
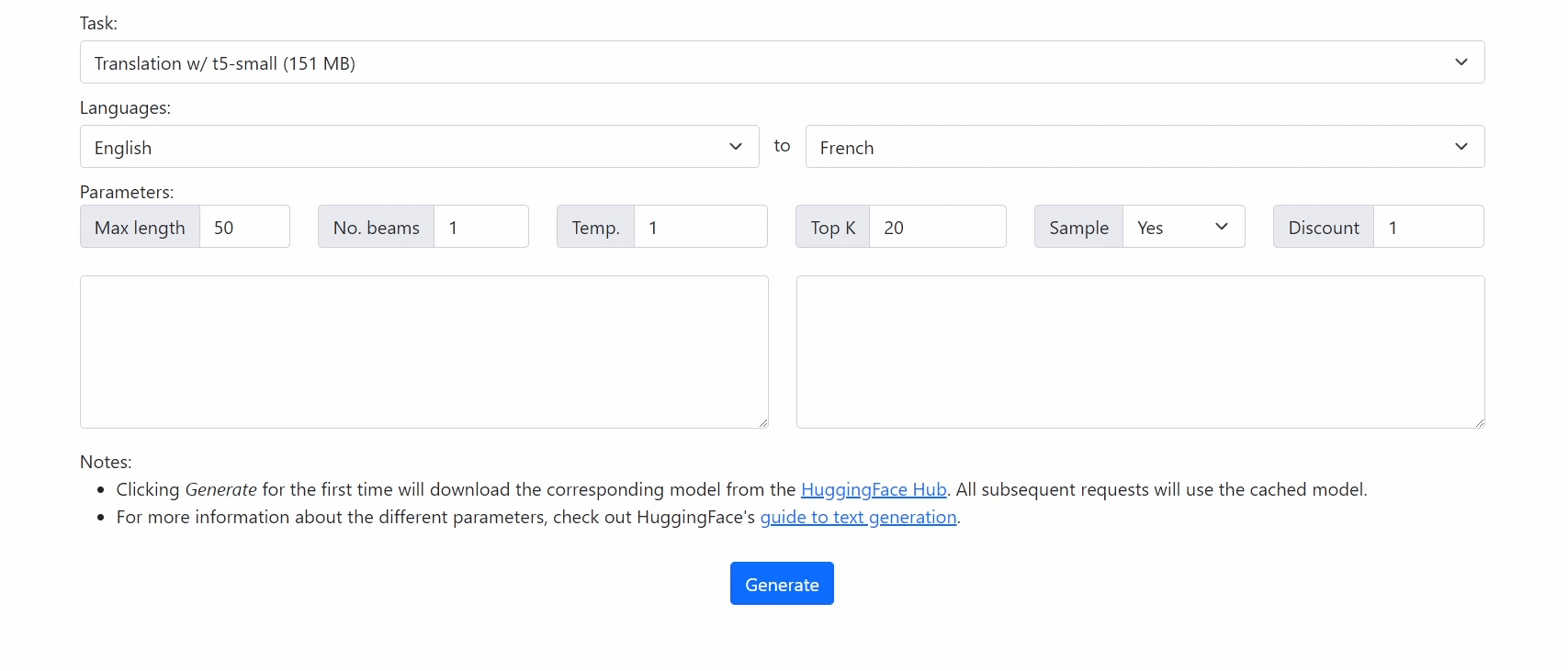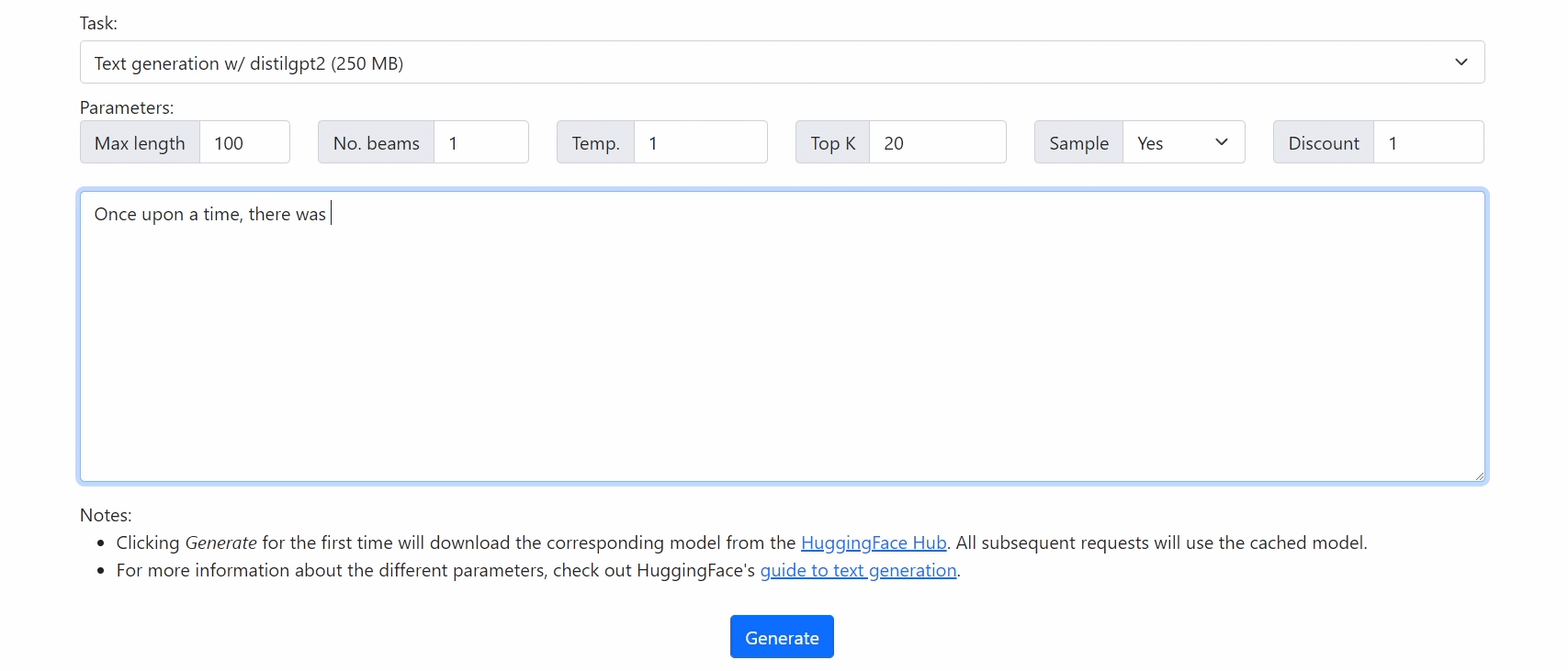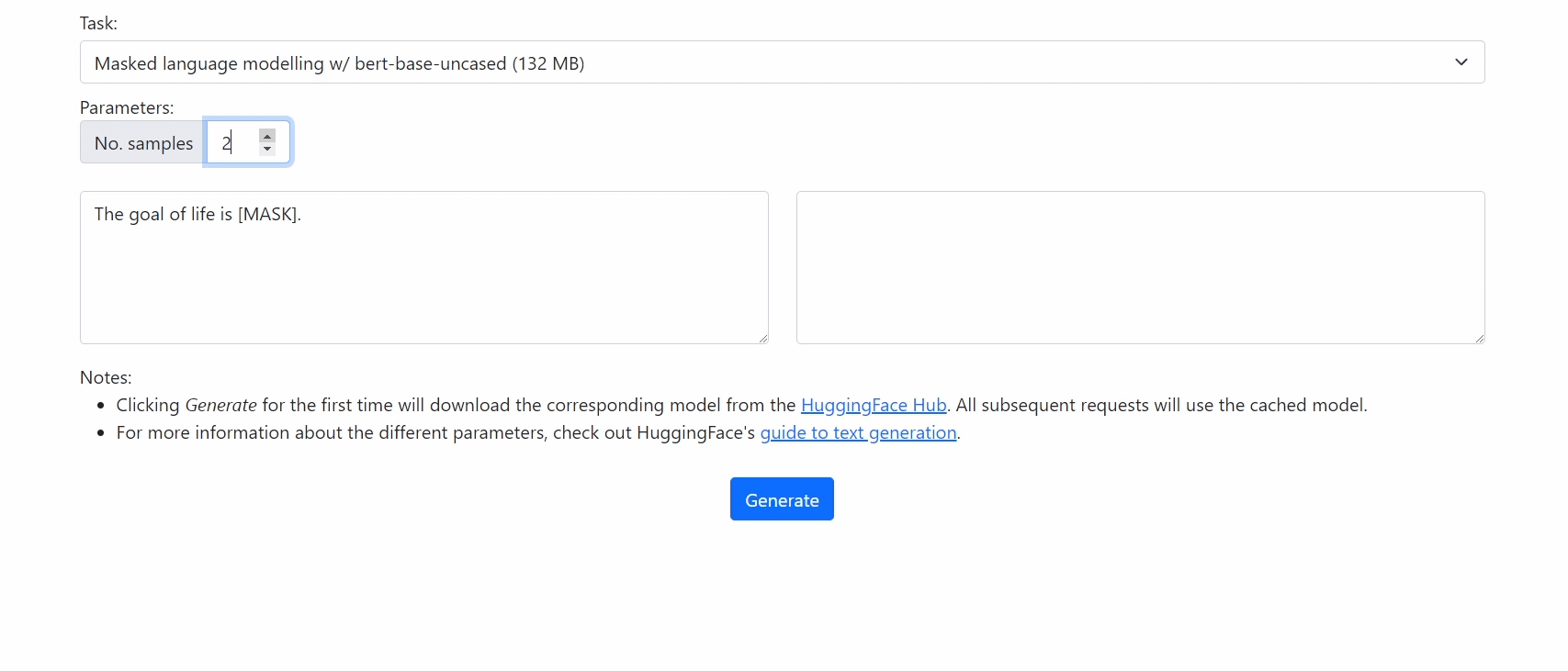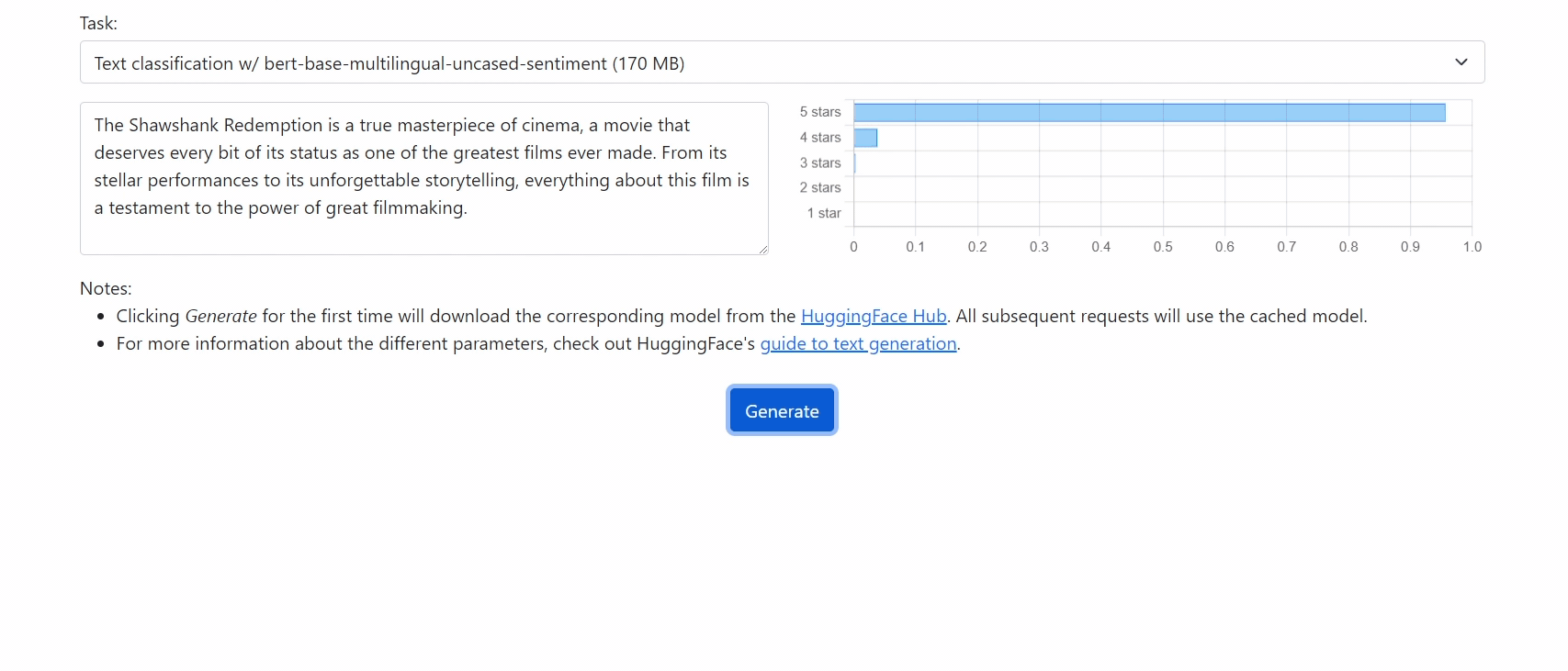
Check out our demo at https://xenova.github.io/transformers.js/. As you'll see, everything runs inside the browser!
If you use npm, you can install it using:
npm i @xenova/transformers
Alternatively, you can use it in a <script> tag from a CDN, for example:
<!-- Using jsDelivr -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@xenova/transformers/dist/transformers.min.js"></script>
<!-- or UNPKG -->
<script src="https://www.unpkg.com/@xenova/transformers/dist/transformers.min.js"></script>
It's super easy to translate from existing code!
| Python (original) | Javascript (ours) |
|---|---|
|
|
In the same way as the Python library, you can use a different model by providing its name as the second argument to the pipeline function. For example:
// Use a different model for sentiment-analysis
let pipe = await pipeline('sentiment-analysis', 'nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment');
By default, Transformers.js uses hosted models and precompiled WASM binaries, which should work out-of-the-box. You can override this behaviour as follows:
import { env } from "@xenova/transformers";
// Use a different host for models.
// - `remoteURL` defaults to use the HuggingFace Hub
// - `localURL` defaults to '/models/onnx/quantized/'
env.remoteURL = 'https://www.example.com/';
env.localURL = '/path/to/models/';
// Set whether to use remote or local models. Defaults to true.
// - If true, use the path specified by `env.remoteURL`.
// - If false, use the path specified by `env.localURL`.
env.remoteModels = false;
// Set parent path of .wasm files. Defaults to use a CDN.
env.onnx.wasm.wasmPaths = '/path/to/files/';
This library uses onnxruntime-web as its default backend. However, if your application runs with Node.js, you can install onnxruntime-node in your project (using npm i onnxruntime-node) to obtain a massive boost in performance (>5x in some cases). The CPU execution provider is much faster than WASM executor provider, most likely due to this issue.
We use ONNX Runtime to run the models in the browser, so you must first convert your PyTorch model to ONNX (which can be done using our conversion script). In general, the command will look something like this:
python -m scripts.convert --model_id <hf_model_id> --from_hub --quantize --task <task>
For example, to use bert-base-uncased for masked language modelling, you can use the command:
python -m scripts.convert --model_id bert-base-uncased --from_hub --quantize --task masked-lm
If you want to use a local model, remove the --from_hub flag from above and place your PyTorch model in the ./models/pytorch/ folder. You can also choose a different location by specifying the parent input folder with --input_parent_dir /path/to/parent_dir/ (note: without the model id).
Alternatively, you can find some of the models we have already converted here. For example, to use bert-base-uncased for masked language modelling, you can use the model found at https://huggingface.co/Xenova/transformers.js/tree/main/quantized/bert-base-uncased/masked-lm.
Note: We recommend quantizing the model (--quantize) to reduce model size and improve inference speeds (at the expense of a slight decrease in accuracy). For more information, run the help command: python -m scripts.convert -h.
Coming soon...
Coming soon... In the meantime, check out the source code for the demo here.
Inspired by https://github.com/praeclarum/transformers-js
FAQs
State-of-the-art Machine Learning for the web. Run 🤗 Transformers directly in your browser, with no need for a server!
The npm package @xenova/transformers receives a total of 65,367 weekly downloads. As such, @xenova/transformers popularity was classified as popular.
We found that @xenova/transformers demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.

Security News
React's CRA deprecation announcement sparked community criticism over framework recommendations, leading to quick updates acknowledging build tools like Vite as valid alternatives.

Security News
Ransomware payment rates hit an all-time low in 2024 as law enforcement crackdowns, stronger defenses, and shifting policies make attacks riskier and less profitable.