
Research
Security News
Quasar RAT Disguised as an npm Package for Detecting Vulnerabilities in Ethereum Smart Contracts
Socket researchers uncover a malicious npm package posing as a tool for detecting vulnerabilities in Etherium smart contracts.
codingdesigner-styles
Advanced tools
npm installnpm run devSCSS is organized into two main folders, with subfolders for different SCSS Components.
$ tree -d -L 3 scss/
scss/
├── _config: for setup and configuration. These files should output no CSS by themselves
│ ├── foundation: set up variables, maps, functions, and mixins for design language
│ │ ├── breakpoints
│ │ ├── colors
│ │ ├── sizes
│ │ ├── typography
│ │ └── z-index
│ ├── layouts
│ ├── utilities: general math and styles calculations
│ │ ├── functions
│ │ └── mixins
│ └── vendor: Place `*.scss` files in here that need to get imported early as vendor styles before others
└── base: App styles. These files output css, using the setup from CONFIG
SCSS Component are in individual subfolders. Not every SCSS Component has or needs every partial file. Some will have more, based on complexity.
scss-component folder
├── _functions.scss: for calculations
├── _map.scss: for structured variables
├── _mixins.scss: SCSS mixins
└── _variables.scss: general SCSS variables.
codingdesigner-styles includes a new layout system based on the new CSS Grid standard, with an optional Flexbox fallback. CSS Grid allows us to create precise layouts with much less code than previous techniques, and many layouts that were impossible, difficult, or brittle previously. There are a few ways to use this system.
This method generates the least amount of compiled CSS and offers the most control over the design. The following code will create a simple 3 column grid.
.some-selector {
@include grid-container();
@include grid-calc-columns(3);
}
With Breakpoint you can add to this to create complex layouts. The following will:
There are also mixins applied to grid items to precisely control where they are placed and how many columns and rows they span at the large width.
.some-selector {
@include grid-container();
@include grid-calc-columns(2, 1em); // arguments: number of columns, gutter width
@include breakpoint(get-breakpoint(md)) {
@include grid-calc-columns(3);
}
@include breakpoint(get-breakpoint(lg)) {
@include grid-calc-columns(20% 1fr 2fr 33%); // arguments: instead of the number of even columns, you can optionally pass in any valid css grid column definition
}
.some-direct-child-selector {
@include breakpoint(get-breakpoint(lg)) {
&:nth-child(1) {
@include grid-item-row-span(3); // The first item will span three rows
}
&:nth-child(2) {
@include grid-item-column-span(2); // This item will span 2 columns
}
&:nth-child(3) {
@include grid-item-row-span(2); // This item will span 2 rows
}
&:nth-child(4) {
@include grid-item-row-span(2); // This item will span 2 rows
}
&:nth-child(5) {
@include grid-item-column-placement(2, 3); // This item will span 2 columns, and is explicitly placed in the 3rd column
@include grid-item-order(6); // This item is moved out of the natural sort order
}
&:nth-child(6) {
@include grid-item-order(5); // This item is moved out of the natural sort order
}
}
}
}

Alternately you can generate a class-based grid framework, with or without the flexbox fallback styles. This will let you create equal-width columns, and control the grid columns, items, and responsive characteristics with css classes. Be mindful that generating a grid framework will create more css than necessary for any use case, because it has to cover all potential layout use cases.
Classes for grid containers:
.grid-container - establishes a grid container.cols-1, .cols-2, .cols-3, etc - sets how many columns in a grid.sm-cols-2, .sm-cols-3, .md-cols-3, .md-cols-4, .lg-cols-4, .xl-cols-6, etc - sets how many columns at different responsive breakpointsClasses for grid items:
.grid-item - only needed when using flex fallback.span-2, .span-3, etc - sets how many columns to span.md-span-2, .lg-span-3, etc - sets how many columns to span at different responsive breakpoints.row-span-2, .row-span-3, etc - sets how many rows to span - not available in flexbox.md-row-span-2, .lg-row-span-3, etc - sets how many rows to span at different responsive breakpoints - not available in flexbox.col-2of4at2 - precisely sets the span and position of an element, in this case the item will span two columns at the second column in a four column grid - available in flexbox, but not in multi-row grids.lg-col-3of6at3 - appending a responsive prefix to the above class will apply precise positioning at different breakpoints - available in flexbox, but not in multi-row grids.order-3, .md-order-3 - order classes and order classes with responsive prefixes let you control the order of grid items
As noted above generating a class-based grid framework comes with certain trade-offs. You gain the ability to layout pages and components using only classes, and do not need to write custom styles or use the provided mixins individually, but you will generate more CSS than you will likely need.
The following settings variables are provided to help limit the generated CSS to the needs of your project.
$grid-gap: 2em; - the default gutter between grid items$use-flex-fallback: false; - set to true if you require flexbox support (for older IE primarily)$generate-grid-framework: false; - set to true if you want to generate a class based grid system$generate-advanced-flex-layouts: false; - experimental set to true if you are using the flex fallback AND you want it to attempt to replicate some of the precise positioning features of css grid$generated-items-max-flexbox: 10; - the number of grid items classes for the flexbox fallback. Only needed when using advanced flex layouts$generated-cols-max: 12; - the number of columns generated. Set this to the smallest number you need.tldr; SCSS extends are not included, and are discouraged in practice.
The use of SCSS @extends is a slightly contentious debate in Sass. I've come down on the “use extends as little as necessary” camp because anything an extend can do, a mixin can also do, with roughly the same amount of generated css. And because extends break when used in media queries, and balloon the css when applied to base elements I discourage them.
Hugo Giraudel on Sass @extends
The CSS properties are sorted using the “Concentric” property sort order, which may be the sort order that best follows the box model. The properties start from the outside of the box and work their way in, as outlined in Brandon Rhodes' Post.
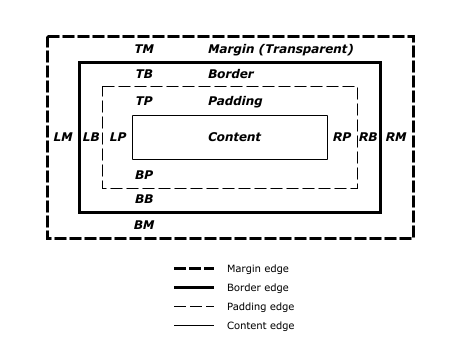
Simplified concentric template
{
display: ; /* Where and how the box is placed */
position: ;
float: ;
clear: ;
visibility: ; /* Can the box be seen? */
opacity: ;
z-index: ;
margin: ; /* Layers of the box model */
outline: ;
border: ;
background: ;
padding: ;
width: ; /* Content dimensions and scrollbars */
height: ;
overflow: ;
color: ; /* Text */
text: ;
font: ;
}
Each SCSS partial is commented using the syntax to generate documentation in SassDoc. Running npm run validate:sass or npm run watch:sass will generate the docs. Running npm run browserSync will start a server to display the docs.
FAQs
## Get Started - `npm install` - `npm run dev`
The npm package codingdesigner-styles receives a total of 3 weekly downloads. As such, codingdesigner-styles popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that codingdesigner-styles demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers uncover a malicious npm package posing as a tool for detecting vulnerabilities in Etherium smart contracts.

Security News
Research
A supply chain attack on Rspack's npm packages injected cryptomining malware, potentially impacting thousands of developers.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers discovered a malware campaign on npm delivering the Skuld infostealer via typosquatted packages, exposing sensitive data.