
Research
Security News
Quasar RAT Disguised as an npm Package for Detecting Vulnerabilities in Ethereum Smart Contracts
Socket researchers uncover a malicious npm package posing as a tool for detecting vulnerabilities in Etherium smart contracts.
corbel-composr
Advanced tools
Composr is a middleware based in nodeJS with restify, to offer developers to make his own specific application API.

#Composr
Composr is a nodeJS opinionated server for executing dinamically created endpoints, it's original purpose is to serve as a middleware for the Corbel - microservices generic backend - , but it's capabilities are growing.
It uses the composr-core API for executing random pieces of code that the developers pushes to the Composr API. This random pieces of code, called Phrases or Snippets are model definitions for endpoints and reusable utilities.
When working with a microservices backend lot of requests have to be grouped together in a "business logic" middleware, Composr serves this purpose. It also adds a bit of coolness.
install
npm install -g bq/corbel-composr
run server
corbel-composr
One way of starting composr is using it as a command, corbel-composr.
This will search for the default configuration under a config folder in the current directory. Composr uses the NPM config module for the configuration. So it will basically search for a development.json file under the config folder.
If NODE_ENV is not set in the environment, a default value of development is used.
{
"serverName" : "CompoSR",
"bodylimit" : "50mb",
"port": 3000,
"rabbitmq": {
"host": "",
"port": "",
"username": "",
"password": "",
"reconntimeout": 10000,
"event": "class com.bq.corbel.event.ResourceEvent",
"forceconnect": false,
"heartbeat" : 30
},
"bootstrap.retrytimeout": 10000,
"services": {
"timeout": 5000,
"retries": 30,
"time": 1000
},
"corbel": {
"credentials": {
"clientId": "",
"clientSecret": "",
"scopes": "composr:comp:base"
},
"options": {
"urlBase": ""
}
},
"redis": {
"host": "localhost",
"port": 6379,
"user": "",
"password": ""
},
"bunyan": {
"log" : true,
"syslog" : true,
"stdout": false,
"streamServer": false
},
"composrLog": {
"accessLog" : true,
"accessLogFile" : "logs/access.log",
"logLevel": "error",
"logFile": "logs/composr.log",
"syslog" : false
},
"newrelic": {
"enabled": false,
"name": "",
"key": ""
},
"keymetrics": true,
"execution": {
"vm": false,
"gc": false,
"timeout": 40000,
"local": false
}
}
Almost all of the vales in the configuration file can be overwriten by environment variables, this can be useful if you use Docker, Travis or any other tool that could send environment variables to configure your server.
SERVER_NAME (Composr 2.0)
PORT (3000)
CREDENTIALS_CLIENT_ID
CREDENTIALS_CLIENT_SECRET
CREDENTIALS_SCOPES
URL_BASE
ACCESS_LOG => winston access log
ACCESS_LOG_FILE => winston access log file
LOG_LEVEL => winston log level
LOG_FILE => winston log file
BUNYAN_LOG(true) => Bunyan logs
BUNYAN_SYSLOG(true) => Send bunyan stream to syslog (127.0.0.1:514)
BUNYAN_STDOUT(false) => Bunyan output in terminal
BUNYAN_STREAM_SERVER (null) => Composr Stream Server endpoint
RABBITMQ_HOST
RABBITMQ_PORT
RABBITMQ_USERNAME
RABBITMQ_PASSWORD
RABBITMQ_FORCE_CONNECT => Only launch composr if rabbit is connected
RABBITMQ_HEARTBEAT => Heartbeat for the rabbitmq connection
REDIS_HOST
REDIS_PORT
REDIS_USER
REDIS_PASSWORD
SERVICES_TIMEOUT
SERVIES_RETRIES
SERVICES_TIME
KEYMETRICS (true) => Keymetrics active
NRACTIVE => New relic active
NRAPPNAME => New relic app name
NRAPIKEY => New relic api key
TIMEOUT=> Endpoint timeout
LOCAL_MODE=>If set to "true" it skips loading the endpoints from a remote server and uses the local files
You can generate and publish your phrases and snippets by using the composr-cli.
npm install -g composr-cli
composr -g
composr init will generate a basic structure for your Phrases project.
Once you bootstrapped some phrases, just run corbel-composr in the current folder and the server will be ready at the port 3000.
Corbel-Composr has a similar routing mechanism than restify. You can define urls by following this conventions:
:param : Url parameteruser : Fixed path valueSome examples
user/:userIduser/status/:parameterthing/one{
"url": "paramsExample/:pathparam",
"get": {
"code": "res.status(200).send('path param: ' + req.params.pathparam + ', query param: ' + req.query.queryparam);"
},
"post": {
/*...*/
},
"put": {
/*...*/
}
}
Composr can take care of multiple endpoints and multiple versions for each endpoint. It uses the semantic versioning for executing different code for each endpoint.
For example, if you published the following phrases to Composr:
{
"url": "user/:userId",
"version": "3.1.0",
"get": { ... }
}
{
"url": "user/:userId",
"version": "4.0.0",
"get": { ... }
}
Then you could request executing the 3.x version by sending the Accept-Version header with a ~3 value, as seen in restify.
Composr autogenerates documentation when navigating to http://localhost:3000/my:domain/doc. The documentation is generated by fulfilling the example documents that composr-cli creates when generating a phrase model.
See an example:
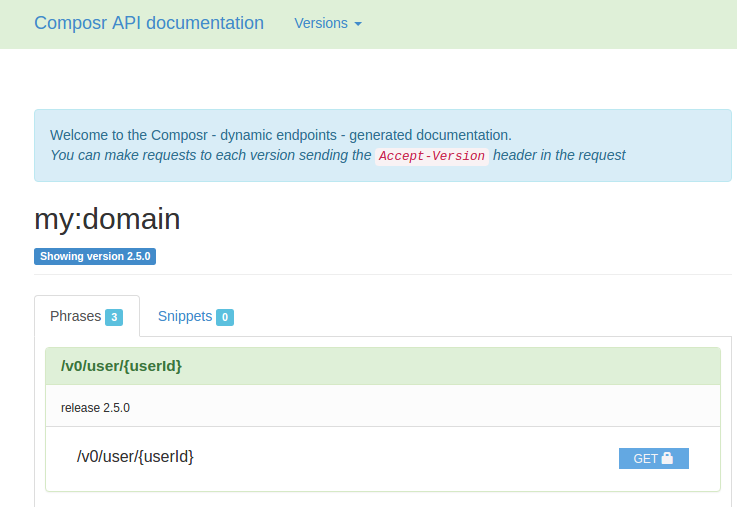
We offer a set of plugable add-ons that will automatically add functionality to your phrases. These middlewares or hooks are executed before or after the code on your phrase. You can specify them on the phrase's spec at a method level like this (order is important!):
{
"url": "resource",
"get": {
"middlewares": [
"auth",
"validate",
"mock"
],
"doc": {
...
}
Among the available middlewares you can find:
Composr instances are connected to a redis machine that serves as a dynamic cache system.
In order to accomplish cache and cache invalidation, phrase models can define some rules:
{
"url": "resource",
"get": {
"middlewares": [
"cache"
],
"cache": {
"type" : "user",
"duration": "5m"
},
"doc": { ... }
}
"post": {
"middlewares": [
"cache"
],
"cache": {
"invalidate": ["get-resource"]
},
"doc": {...}
}
...
}
The phrase model uses the cache middleware in the verbs GET and POST. In the GET method the cache will store in Redis a key for each user with a time to live of five minutes.
When a request is made to the POST method, the cache middleware will hit in, too, but in this case it will invalidate the cache of the GET method for the resource url.
Cache can be used for:
The cache for client request is the most common type of cache, client requests are made with a client token (which refers normally to a public resource), or without token at all.
The cache for user requests should be used carefully because it will create a Redis key-value pair for each user.
Each cached endpoint can have a duration (time to live), some examples of available values are:
1m : 1 minute100ms: 100 miliseconds2h 30mins: 2 hours 30minutes1d: 1 day1w: 1 weekSee parse-duration for valid values
Composr is shipped with built-in bunyan and winston support.
You can set logFile and logLevel in your config file.
Available log levels can be found at winston's npm page:
Bunyan logs are enabled by default. You can disable them by turning bunyan.log to false in your configuration.
npm test
npm run coverage
Requires node-inspector
npm install -g node-inspector
Server
npm run debug --myphrase.get
Tests
npm run test:debug
clone repo
build image
docker build -t <username>/corbel-composr .
run container
docker run -d -p 3000:3000 --name="corbel-composr" <username>/corbel-composr
start/stop container
docker start/stop corbel-composr
A Redis instance, if you want to run it locally with docker:
sudo docker run --name some-redis -p 6379:6379 -d redis
FAQs
Composr is a middleware based in nodeJS with restify, to offer developers to make his own specific application API.
We found that corbel-composr demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers uncover a malicious npm package posing as a tool for detecting vulnerabilities in Etherium smart contracts.

Security News
Research
A supply chain attack on Rspack's npm packages injected cryptomining malware, potentially impacting thousands of developers.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers discovered a malware campaign on npm delivering the Skuld infostealer via typosquatted packages, exposing sensitive data.