Fauton
A library to test and transform any finite automaton with arbitrary alphabets








Please note that I won't be following semver at the initial stages, as there could be a lot of (breaking) changes between each release which will all be patch
Features
- Test any valid dfa/nfa/ε-nfa/regex
- Supports arbitrary alphabets
- Easy to use api to generate input strings
- ε-nfa to nfa conversion
- ε-nfa/nfa to dfa conversion
- Generate artifacts files for each automaton
- Highly customizable
- Full typescript support
- Simple concise error messages for invalid finite automaton
- Generate full graph for ε-nfa given a string
- Generate ε closure of a single state
Motivation
Its easy to check whether a string should be accepted or rejected using our favourite programming languages, but its a lot harder to transfer the logic to a finite automaton. Even if we are quite sure we can't be 100% sure until and unless we try out all the possible combinations of alphabet of the automata. This is an extremely tedious and error-prone process. Why not automate testing an automaton?
Examples
Dfa for string that starts with bc
Lets start out with a simple dfa, that checks whether an input string starts with bc. The alphabets of the dfa are a, b, c

const { DeterministicFiniteAutomaton, FiniteAutomataTest } = require('fauton');
const startsWithBC = new DeterministicFiniteAutomaton(
(inputString) => inputString.startsWith('bc'),
{
alphabets: ['a', 'b', 'c'],
description: 'Starts with bc',
final_states: ['Q3'],
label: 'starts_with_bc',
start_state: 'Q0',
states: ['Q0', 'Q1', 'Q2', 'Q3'],
transitions: {
Q0: ['Q2', 'Q1', 'Q2'],
Q1: ['Q2', 'Q2', 'Q3'],
Q2: 'loop',
Q3: 'loop',
},
}
);
const finiteAutomataTest = new FiniteAutomataTest(path.join(__dirname, 'logs'));
finiteAutomataTest.test([
{
automaton: startsWithBC,
options: {
type: 'generate',
combo: {
maxLength: 10,
},
},
},
]);
Binary string divisible by 2 or 3 but not both
In this case it will be better if we construct two dfa's and merge them together to form the final dfa.
Let D2 be the dfa responsible for checking divisibility by 2 and D3 be responsible for divisibility by 3
Our condition is (D2 OR D3) AND NOT(D2 AND D3), meaning either the string passes through D2 or D3, but not by both. So 2 will be accepted, 3 will be accepted but 6 will be rejected as its divisible by both 2 and 3

Lets generate a new dfa by combining the first two dfa's !!!
const { FiniteAutomataTest, DeterministicFiniteAutomaton } = require('fauton');
const path = require('path');
const DivisibleBy3 = new DeterministicFiniteAutomaton(
(inputString) => parseInt(inputString, 2) % 3 === 0,
{
alphabets: ['0', '1'],
final_states: ['A'],
label: 'divisible_by_3',
start_state: 'A',
states: ['A', 'B', 'C'],
transitions: {
A: ['A', 'B'],
B: ['C', 'A'],
C: ['B', 'C'],
},
description: 'Dfa to accept strings divisible by 3',
}
);
const DivisibleBy2 = new DeterministicFiniteAutomaton(
(inputString) => parseInt(inputString, 2) % 2 === 0,
{
alphabets: ['0', '1'],
final_states: ['X'],
label: 'divisible_by_2',
start_state: 'X',
states: ['X', 'Y'],
transitions: {
X: ['X', 'Y'],
Y: ['X', 'Y'],
},
description: 'Dfa to accept strings divisible by 2',
}
);
const DivisibleBy2Or3 = DivisibleBy2.OR(DivisibleBy3);
const NotDivisibleBy2And3 = DivisibleBy2.AND(DivisibleBy3).NOT();
const DivisibleBy3Or2ButNotByBoth = DivisibleBy2Or3.AND(NotDivisibleBy2And3);
const finiteAutomataTest = new FiniteAutomataTest(path.resolve(__dirname, 'logs'));
finiteAutomataTest.test([
{
automaton: DivisibleBy3Or2ButNotByBoth,
options: {
type: 'generate',
combo: {
maxLength: 10,
},
},
},
]);
console.log(DivisibleBy3Or2ButNotByBoth.automaton.transitions);
console.log(DivisibleBy3Or2ButNotByBoth.automaton.start_state);
console.log(DivisibleBy3Or2ButNotByBoth.automaton.final_states);
> {
'X.A': { '0': [ 'X.A' ], '1': [ 'Y.B' ] },
'Y.A': { '0': [ 'X.A' ], '1': [ 'Y.B' ] },
'X.B': { '0': [ 'X.C' ], '1': [ 'Y.A' ] },
'Y.B': { '0': [ 'X.C' ], '1': [ 'Y.A' ] },
'X.C': { '0': [ 'X.B' ], '1': [ 'Y.C' ] },
'Y.C': { '0': [ 'X.B' ], '1': [ 'Y.C' ] }
}
> X.A
> [ 'Y.A', 'X.B', 'X.C' ]
It automatically generates the merged transitions, new start and final states
Nfa for string that starts with ab

const { NonDeterministicFiniteAutomaton, FiniteAutomataTest } = require('fauton');
const path = require('path');
const startsWithAB = new NonDeterministicFiniteAutomaton(
(inputString) => inputString.startsWith('ab'),
{
alphabets: ['a', 'b', 'c'],
description: 'Starts with ab',
final_states: ['C'],
label: 'starts_with_ab',
start_state: 'A',
states: ['A', 'B', 'C'],
transitions: {
A: ['B'],
B: [null, 'C'],
C: 'loop',
},
}
);
const finiteAutomataTest = new FiniteAutomataTest(path.join(__dirname, 'logs'));
finiteAutomataTest.test([
{
automaton: startsWithAB,
options: {
type: 'generate',
combo: {
maxLength: 10,
},
},
},
]);
ε-nfa to nfa
Lets say we have the following ε-nfa, and we want to convert it to nfa

const { NonDeterministicFiniteAutomaton } = require('fauton');
const path = require('path');
const randomEpsilonNFA = new NonDeterministicFiniteAutomaton(
(inputString) => inputString.startsWith('ab'),
{
alphabets: ['a', 'b', 'c'],
description: 'Starts with ab',
final_states: ['C'],
label: 'random_epsilon_nfa',
start_state: 'A',
states: ['A', 'B', 'C'],
transitions: {
A: ['B', null, 'B'],
B: [null, 'C'],
C: [null, null, 'C'],
},
epsilon_transitions: {
A: ['B'],
},
}
);
console.log(randomEpsilonNFA.automaton.transitions);
{
A: { a: [ 'B', 'C' ], c: [ 'B', 'C' ], b: [ 'C' ] },
B: { b: [ 'C' ], a: [], c: [ 'C' ] },
C: { c: [ 'C' ] }
}
Generate and render full graph for a ε-nfa given a string
const { NonDeterministicFiniteAutomaton, Render } = require('fauton');
const path = require('path');
const randomEpsilonNFA = new NonDeterministicFiniteAutomaton(
(inputString) => inputString.startsWith('ab'),
{
alphabets: ['a', 'b', 'c'],
description: 'Starts with ab',
final_states: ['C'],
label: 'random_epsilon_nfa',
start_state: 'A',
states: ['A', 'B', 'C'],
transitions: {
A: ['B', 'C', 'B'],
B: ['A', 'C'],
C: ['A', null, 'C'],
},
epsilon_transitions: {
A: ['B'],
B: ['C'],
},
}
);
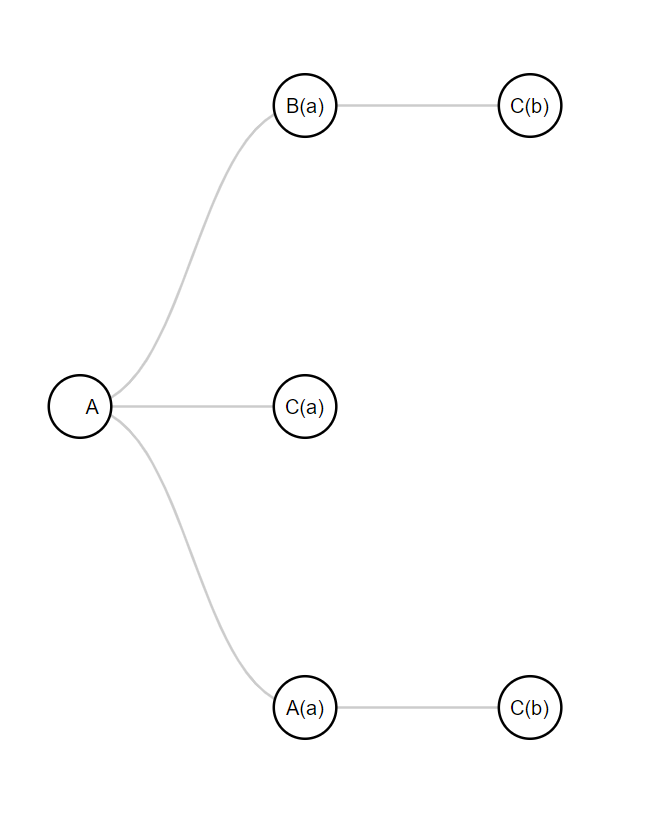
const { graph } = randomEpsilonNFA.generateGraphFromString('abbc');
console.log(JSON.stringify(graph, null, 2));
Render.graphToHtml(graph, path.join(__dirname, 'index.html'));
{
"name": "A",
"state": "A",
"string": "",
"depth": 0,
"symbol": null,
"children": [
{
"name": "B(a)",
"state": "B",
"string": "a",
"depth": 1,
"symbol": "a",
"children": [
{
"name": "C(b)",
"state": "C",
"string": "ab",
"depth": 2,
"symbol": "b",
"children": []
}
]
},
{
"name": "C(a)",
"state": "C",
"string": "a",
"depth": 1,
"symbol": "a",
"children": []
},
{
"name": "A(a)",
"state": "A",
"string": "a",
"depth": 1,
"symbol": "a",
"children": [
{
"name": "C(b)",
"state": "C",
"string": "ab",
"depth": 2,
"symbol": "b",
"children": []
}
]
}
]
}
Generated d3 graph
Conversion from ε-nfa to dfa
const { NonDeterministicFiniteAutomaton } = require('fauton');
const epsilonNfa = new NonDeterministicFiniteAutomaton((_, automatonTest) => automatonTest, {
start_state: 0,
alphabets: ['a', 'b'],
final_states: [10],
label: 'sample ε nfa',
states: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
transitions: {
2: [3],
4: [null, 5],
7: [8],
8: [null, 9],
9: [null, 10],
},
epsilon_transitions: {
0: [1, 7],
1: [2, 4],
3: [6],
5: [6],
6: [1, 7],
},
});
console.log(JSON.stringify(epsilonNfa.convertToDeterministicFiniteAutomaton(), null, 2));
{
"automaton": {
"alphabets": ["a", "b"],
"final_states": ["0,1,10,2,4,5,6,7"],
"label": "sample ε nfa",
"start_state": "0,1,2,4,7",
"states": ["0,1,2,4,7", "1,2,3,4,6,7,8", "1,2,4,5,6,7", "1,2,4,5,6,7,9", "0,1,10,2,4,5,6,7"],
"transitions": {
"0,1,2,4,7": {
"a": ["1,2,3,4,6,7,8"],
"b": ["1,2,4,5,6,7"]
},
"1,2,3,4,6,7,8": {
"a": ["1,2,3,4,6,7,8"],
"b": ["1,2,4,5,6,7,9"]
},
"1,2,4,5,6,7": {
"a": ["1,2,3,4,6,7,8"],
"b": ["1,2,4,5,6,7"]
},
"1,2,4,5,6,7,9": {
"a": ["1,2,3,4,6,7,8"],
"b": ["0,1,10,2,4,5,6,7"]
},
"0,1,10,2,4,5,6,7": {
"a": ["1,2,3,4,6,7,8"],
"b": ["1,2,4,5,6,7"]
}
},
"epsilon_transitions": null
}
}
Conversion from nfa to dfa
const { NonDeterministicFiniteAutomaton } = require('fauton');
const nfa = new NonDeterministicFiniteAutomaton((_, automatonTest) => automatonTest, {
start_state: 'q0',
alphabets: ['a', 'b'],
final_states: ['q1'],
label: 'sample nfa',
states: ['q0', 'q1', 'q2'],
transitions: {
q0: [['q2', 'q1']],
q2: [['q2', 'q1'], 'q2'],
},
});
console.log(JSON.stringify(nfa.convertToDeterministicFiniteAutomaton(), null, 2));
{
"automaton": {
"alphabets": ["a", "b"],
"final_states": ["q1,q2"],
"label": "sample nfa",
"start_state": "q0",
"states": ["q0", "q1,q2", "Ø", "q2"],
"transitions": {
"q0": {
"a": ["q1,q2"],
"b": ["Ø"]
},
"q1,q2": {
"a": ["q1,q2"],
"b": ["q2"]
},
"q2": {
"a": ["q1,q2"],
"b": ["q2"]
},
"Ø": {
"a": ["Ø"],
"b": ["Ø"]
}
},
"epsilon_transitions": null
}
}
Dfa minimization
const { DeterministicFiniteAutomaton } = require('fauton');
const dfa = new DeterministicFiniteAutomaton(() => true, {
states: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
alphabets: ['0', '1'],
final_states: [2],
start_state: 0,
label: 'dfa',
transitions: {
0: [1, 5],
1: [6, 2],
2: [0, 2],
3: [2, 6],
4: [7, 5],
5: [2, 6],
6: [6, 4],
7: [6, 2],
},
});
console.log(dfa.minimize().automaton);
{
"label": "dfa",
"alphabets": ["0", "1"],
"final_states": ["2"],
"start_state": "04",
"states": ["04", "35", "17", "6", "2"],
"transitions": {
"2": {
"0": ["04"],
"1": ["2"]
},
"6": {
"0": ["6"],
"1": ["04"]
},
"17": {
"0": ["6"],
"1": ["2"]
},
"35": {
"0": ["2"],
"1": ["6"]
},
"04": {
"0": ["17"],
"1": ["35"]
}
},
"epsilon_transitions": null
}
Dfa equivalency by testing
Testing if two dfa are equal through testing. One of the dfa is the minimized version of the other dfa, all the input string should return similar test result for both of them.
import { DeterministicFiniteAutomaton, FiniteAutomataTest, FiniteAutomatonUtils } from 'fauton';
import path from 'path';
const dfa = new DeterministicFiniteAutomaton(() => true, {
states: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
alphabets: ['0', '1'],
final_states: [2],
start_state: 0,
label: 'dfa',
transitions: {
0: [1, 5],
1: [6, 2],
2: [0, 2],
3: [2, 6],
4: [7, 5],
5: [2, 6],
6: [6, 4],
7: [6, 2],
},
});
const minimized_dfa = dfa.minimize();
minimized_dfa.testLogic = (inputString) => {
return FiniteAutomatonUtils.generateGraphFromString(dfa.automaton, inputString)
.automatonTestResult;
};
const finiteAutomataTest = new FiniteAutomataTest(path.join(__dirname, 'logs'));
finiteAutomataTest.test([
{
automaton: minimized_dfa,
options: {
type: 'generate',
combo: {
maxLength: 10,
},
},
},
]);
Testing regular expressions
Rather than testing only a finite automaton, you can also test your regular expressions against generated strings
import { FiniteAutomataTest, RegularExpression } from 'fauton';
import path from 'path';
const regex = new RegularExpression(
(inputString) => {
return (
inputString[0] === 'a' &&
inputString[1] === 'b' &&
inputString
.slice(2)
.split('')
.every((char) => char === 'c')
);
},
{
alphabets: ['a', 'b', 'c'],
label: 'Starts with a and b, ends with any number of c',
regex: /^abc*$/g,
}
);
const finiteAutomataTest = new FiniteAutomataTest(path.join(__dirname, 'logs'));
finiteAutomataTest.test([
{
automaton: regex,
options: {
type: 'generate',
combo: {
maxLength: 10,
},
},
},
]);
Take a look at examples folder for more examples.
Conditions for DFA
Deterministic finite automaton must follow certain conditions for it to be considered as one. These are described below
transitions record must contain all the elements of states array as its key- Only the items of the
states can be the key of the transitions record transitions record values must either be an array or the string literal loop- If its an array its length should be the same
alphabets array, where each index represents which state to transition to when encountering a symbol (index of the alphabets array) - Also if its an array each item should be a string as for a single symbol a dfa can transition to only one state
transitions record values can only have symbols that are present in the alphabets array
Transitions Record Transformation
dfa
All the states of the dfa must have transitions for all the input symbols.
{
"final_states": ["A", "B", "C"],
"alphabets": ["0", "1", "2"],
"transitions": {
"A": ["B", "C", "A"],
"B": ["C", "A", "C"],
"C": "loop"
}
}
For the above automaton, the transitions record will be transformed like the following:-
{
"A": {
"0": "B",
"1": "C",
"2": "A",
},
"B": {
"0": "C",
"1": "A",
"2": "C",
},
"C": {
"0": "C",
"1": "C",
"2": "C",
},
};
nfa
{
"alphabets": ["a", "b", "c"],
"states": ["A", "B", "C"],
"transitions": {
"A": ["B", null, "B"],
"B": [null, "C"],
"C": [null, null, "C"]
}
}
Since its a nfa the conditions of transitions record for dfa is not applicable here
{
"A": {
"a": ["B"],
"c": ["B"]
},
"B": {
"b": ["C"]
},
"C": {
"c": ["C"]
}
}
ε-nfa
{
"alphabets": ["a", "b", "c"],
"states": ["A", "B", "C"],
"transitions": {
"A": ["B", null, "B"],
"B": [null, "C"],
"C": [null, null, "C"]
},
"epsilon_transitions": {
"A": ["B"]
}
}
Transformed transitions record
{
A: { a: [ 'B', 'C' ], c: [ 'B', 'C' ], b: [ 'C' ] },
B: { b: [ 'C' ], a: [], c: [ 'C' ] },
C: { c: [ 'C' ] }
}
Input string generation
When testing the finite automaton using the FiniteAutomataTest class object's test method there are four ways to provide input strings to the automaton and the logic test callback
Reading from a file
If you already have a file that contains a bunch of input strings made of valid symbols of the automata you can load that file and feed each strings (delimited by a newline) to the automata and logic test.
finiteAutomataTest.test([
{
automaton,
options: {
type: 'file',
filePath: path.join(__dirname, 'input.txt'),
},
},
]);
Custom array of strings
You can provide your own custom array of strings to feed to the automaton and logic test callback.
finiteAutomataTest.test([
{
automaton,
options: {
type: 'custom',
inputs: ['101', '110', '00101'],
},
},
]);
Generating random strings
You can feed automaton and logic test callback a set of unique randomly generated strings from the alphabet of the automaton
finiteAutomataTest.test([
{
automaton,
options: {
type: 'generate',
random: {
maxLength: 4,
minLength: 2,
total: 5,
},
},
},
]);
Generating all combinations of certain length
You can feed automata and logic test callback a set of unique randomly generated strings from the alphabet of the automata
finiteAutomataTest.test([
{
automaton,
options: {
type: 'generate',
combo: {
maxLength: 3,
},
},
},
]);
If you alphabet is a,b then it will generate the following set of strings
a, b, aa, bb, ab, ba, aaa, aab, aba, abb, bbb, bba, bab, baa
Generated artifact files
After running the test, artifact files will be generated in the folder specified in the FiniteAutomataTest class constructor. These files contain additional information about the test and starts with the label of the dfa.
Sample artifact files
Sample artifact files shown inside logs directory

<fa.label>.accepted.txt
Contains all the strings that will be accepted by the automaton

<fa.label>.aggregate.txt
Contains an aggregated result of the test. Its similar to what is shown in the terminal. See Terminal Output

<fa.label>.case.txt
Contains detailed results for each input string test case.

- Result:
CORRECT if fa.result == logic.result, WRONG otherwise - String: Input string
- Logic:
logic.result - FA:
fa.result
<fa.label>.correct.txt
Contains all the strings that generated the same boolean result from the logic test callback and the automaton.

- First column:
fa.result - Second column:
logic.result - Third column: Input string
<fa.label>.incorrect.txt
Contains all the strings that generated different boolean result from the logic test callback and the automaton
Same as <fa.label>.correct.txt
<fa.label>.input.txt
Contains all the input strings. Useful when you are generating random or combo strings and want to reuse it for later
Same as <fa.label>.accepted.txt
<fa.label>.rejected.txt
Contains all the strings that have been rejected by the automaton
Same as <fa.label>.accepted.txt
Terminal Output
While the test is proceeding the progress will be shown in the terminal, and once its done an aggregated result of the test will be shown as below.
Sample terminal output

fa.result: Indicates the result from the finite automatalogic.result: Indicates the result from the logic test
The progress bar shows the number of input strings that's been processed. Beneath that the label, description and the total number of input strings are shown
Incorrect Portion
Incorrect: Total number of strings where the automaton and logic test gave different result. Conditions:-
fa.result = false && logic.result = truefa.result = true && logic.result = false
Incorrect(%): Percentage of strings that are incorrect out of all stringsFalse Positives: Total number of strings that didn't pass the logic test but passed the automata test. Condition:-
fa.result = true && logic.result = false
False Positives(%): Total number of false positives out of all stringsFalse Negatives: Total number of strings that passed the logic test but didn't pass the automata test. Condition:-
fa.result = false && logic.result = true
False Negatives(%): Total number of false negatives out of all strings
Correct Portion
Correct: Total number of strings where the automaton and logic test gave same result. Conditions:-
fa.result = true && logic.result = truefa.result = false && logic.result = false
Correct(%): Percentage of strings that are correct out of all stringsTrue Positives: Total number of strings that passed both the logic and automata test. Condition:-
fa.result = true && logic.result = true
True Positives(%): Total number of true positives out of all stringsTrue Negatives: Total number of strings that didn't pass both the logic and automata test. Condition:-
fa.result = false && logic.result = false
True Negatives(%): Total number of true negatives out of all strings
Better and more detailed api documentation coming soon very soon !!!
Contributors
- Safwan Shaheer github Author, Maintainer
Algorithm Sources
Wikipedia sources for all the algorithms used in the package
- Thompson-McNaughton-Yamada algorithm for converting regex to e-nfa
- Hopcroft algorithm for dfa-minimization
- Rabin–Scott powerset construction algorithm to convert nfa to dfa
- Shunting-Yard algorithm to convert regex string from infix to postfix
Credits
Big thanks to all these wonderful repos.
- Orban Regular expression engine that uses the Thompson-McNaughton-Yamada algorithm implemented in Python.
Feel free to submit a pull request or open a new issue, contributions are more than welcome !!!





















