


New Relic React Native Agent
This agent uses native New Relic Android and iOS agents to instrument the React-Native Javascript environment. The New Relic SDKs collect crashes, network traffic, and other information for hybrid apps using native components.
Features
- Capture JavaScript errors
- Network Instrumentation
- Distributed Tracing
- Tracking console log, warn and error
- Promise rejection tracking
- Capture interactions and the sequence in which they were created
- Pass user information to New Relic to track user sessions
- Expo Support (Bare Workflow & Managed Workflow)
Current Support:
- Android API 24+
- iOS 10
- Depends on New Relic iOS/XCFramework and Android agents
Native support levels are based on React Native requirements.
Requirements
Installation
Yarn
yarn add newrelic-react-native-agent
NPM
npm i newrelic-react-native-agent
React Native Setup
Now open your index.js and add the following code to launch NewRelic (don't forget to put proper application tokens):
import NewRelic from 'newrelic-react-native-agent';
import * as appVersion from './package.json';
import {Platform} from 'react-native';
let appToken;
if (Platform.OS === 'ios') {
appToken = '<IOS-APP-TOKEN>';
} else {
appToken = '<ANDROID-APP-TOKEN>';
}
const agentConfiguration = {
analyticsEventEnabled: true,
nativeCrashReportingEnabled: true,
crashReportingEnabled: true,
interactionTracingEnabled: false,
networkRequestEnabled: true,
networkErrorRequestEnabled: true,
httpResponseBodyCaptureEnabled: true,
loggingEnabled: true,
logLevel: NewRelic.LogLevel.INFO,
webViewInstrumentation: true,
offlineStorageEnabled:true,
backgroundReportingEnabled:false,
newEventSystemEnabled:false,
distributedTracingEnabled: true,
};
NewRelic.startAgent(appToken,agentConfiguration);
NewRelic.setJSAppVersion(appVersion.version);
AppRegistry.registerComponent(appName, () => App);
AppToken is platform-specific. You need to generate the seprate token for Android and iOS apps.
Android Setup
-
Install the New Relic native Android agent (instructions here).
-
Add the following changes to Apply Gradle Plugin:
If you are using Plugins DSL to Apply the NewRelic Gradle Plugin, make the following changes:
In android/settings.gradle:
plugins {
id "com.android.application" version "7.4.2" apply false
id "org.jetbrains.kotlin.android" version "1.7.10" apply false
id "com.newrelic.agent.android" version "7.5.1" apply false // <-- include this
}
In android/app/build.gradle:
plugins {
id "com.android.application"
id "kotlin-android"
id "com.newrelic.agent.android" //<-- include this
}
Or, if you are using the traditional way to apply the plugin:
buildscript {
...
repositories {
...
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
...
classpath "com.newrelic.agent.android:agent-gradle-plugin:7.5.1"
}
}
Apply the NewRelic plugin to the top of the android/app/build.gradle file:
apply plugin: "com.android.application"
apply plugin: 'newrelic' // <-- include this
- Make sure your app requests INTERNET and ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE permissions by adding these lines to your
AndroidManifest.xml
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
iOS Setup
Run the following, and it will install the New Relic XCFramework agent:
npx pod-install
AutoLinking and rebuilding
- Once the above steps have been completed, the React Native NewRelic library must be linked to your project and your application needs to be rebuilt.
If you use React Native 0.60+, you automatically have access to "autolinking," requiring no further manual installation steps.
To automatically link the package, rebuild your project:
# Android apps
npx react-native run-android
# iOS apps
cd ios/
pod install --repo-update
cd ..
npx react-native run-ios
If you run following commands then Fatal JS erros will show up as a crash in NR.
npx react-native run-ios --configuration Release
npx react-native run-android --variant=release
Expo
Integration with Expo is possible in both bare workflow and custom managed workflow via config plugins.
Routing Instrumentation
We currently provide two routing instrumentations out of the box to instrument route changes for and route changes record as Breadcrumb.
Alternatively, you can report your screen changes manually using the following API:
var params = {
'screenName':'screenName'
};
NewRelic.recordBreadcrumb('navigation',params);
Usage
See the examples below, and for more detail, see New Relic IOS SDK doc or Android SDK.
startInteraction(interactionName: string): Promise<InteractionId>;
Track a method as an interaction.
InteractionId is string.
Name or rename interaction (Android-specific).
End an interaction
(Required). This uses the string ID for the interaction you want to end.
This string is returned when you use startInteraction().
const badApiLoad = async () => {
const interactionId = await NewRelic.startInteraction('StartLoadBadApiCall');
console.log(interactionId);
const url = 'https://facebook.github.io/react-native/moviessssssssss.json';
fetch(url)
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((responseJson) => {
console.log(responseJson);
NewRelic.endInteraction(interactionId);
}) .catch((error) => {
NewRelic.endInteraction(interactionId);
console.error(error);
});;
};
setAttribute(name: string, value: boolean | number | string): void;
Creates a session-level attribute shared by multiple mobile event types. Overwrites its previous value and type each time it is called.
NewRelic.setAttribute('RNCustomAttrNumber', 37);
removeAttribute(name: string, value: boolean | number | string): void;
This method removes the attribute specified by the name string..
NewRelic.removeAttribute('RNCustomAttrNumber');
incrementAttribute(name: string, value?: number): void;
Increments the count of an attribute with a specified name. Overwrites its previous value and type each time it is called. If the attribute does not exists, it creates a new attribute. If no value is given, it increments the value by 1.
NewRelic.incrementAttribute('RNCustomAttrNumber');
NewRelic.incrementAttribute('RNCustomAttrNumber', 5);
setUserId(userId: string): void;
Set a custom user identifier value to associate user sessions with analytics events and attributes.
NewRelic.setUserId("RN12934");
recordBreadcrumb(name: string, attributes?: {[key: string]: any}): void;
Track app activity/screen that may be helpful for troubleshooting crashes.
NewRelic.recordBreadcrumb("shoe", {"shoeColor": "blue","shoesize": 9,"shoeLaces": true});
recordCustomEvent(eventType: string, eventName?: string, attributes?: {[key: string]: any}): void;
Creates and records a custom event for use in New Relic Insights.
NewRelic.recordCustomEvent("mobileClothes", "pants", {"pantsColor": "blue","pantssize": 32,"belt": true});
crashNow(message?: string): void;
Throws a demo run-time exception to test New Relic crash reporting.
NewRelic.crashNow();
NewRelic.crashNow("New Relic example crash message");
Returns the current session ID. This method is useful for consolidating monitoring of app data (not just New Relic data) based on a single session definition and identifier.
let sessionId = await NewRelic.currentSessionId();
noticeHttpTransaction(url: string, httpMethod: string, statusCode: number, startTime: number, endTime: number, bytesSent: number, bytesReceived: number, responseBody: string): void;
Tracks network requests manually. You can use this method to record HTTP transactions, with an option to also send a response body.
NewRelic.noticeHttpTransaction('https://github.com', 'GET', 200, Date.now(), Date.now()+1000, 100, 101, "response body");
noticeNetworkFailure(url: string, httpMethod: string, startTime: number, endTime: number, failure: string): void;
Records network failures. If a network request fails, use this method to record details about the failures. In most cases, place this call inside exception handlers, such as catch blocks.
NewRelic.noticeNetworkFailure('https://github.com', 'GET', Date.now(), Date.now(), NewRelic.NetworkFailure.BadURL);
recordMetric(name: string, category: string, value?: number, countUnit?: string, valueUnit?: string): void;
Records custom metrics (arbitrary numerical data), where countUnit is the measurement unit of the metric count and valueUnit is the measurement unit for the metric value. If using countUnit or valueUnit, then all of value, countUnit, and valueUnit must all be set.
NewRelic.recordMetric('RNCustomMetricName', 'RNCustomMetricCategory');
NewRelic.recordMetric('RNCustomMetricName', 'RNCustomMetricCategory', 12);
NewRelic.recordMetric('RNCustomMetricName', 'RNCustomMetricCategory', 13, NewRelic.MetricUnit.PERCENT, NewRelic.MetricUnit.SECONDS);
Removes all attributes from the session
NewRelic.removeAllAttributes();
recordError(e: string|error): void;
Records javascript errors for react-native.
try {
var foo = {};
foo.bar();
} catch(e) {
NewRelic.recordError(e);
}
Sets the event harvest cycle length. Default is 600 seconds (10 minutes). Minimum value can not be less than 60 seconds. Maximum value should not be greater than 600 seconds.
NewRelic.setMaxEventBufferTime(60);
Sets the maximum size of the event pool stored in memory until the next harvest cycle. Default is a maximum of 1000 events per event harvest cycle. When the pool size limit is reached, the agent will start sampling events, discarding some new and old, until the pool of events is sent in the next harvest cycle.
NewRelic.setMaxEventPoolSize(2000);
The following methods allow you to set some agent configurations after the agent has started:
Follow these steps if the agent has not started yet.
FOR ANDROID ONLY. Enable or disable the collecton of event data.
NewRelic.analyticsEventEnabled(true);
Enable or disable reporting successful HTTP requests to the MobileRequest event type.
NewRelic.networkRequestEnabled(true);
Enable or disable reporting network and HTTP request errors to the MobileRequestError event type.
NewRelic.networkErrorRequestEnabled(true);
Enable or disable capture of HTTP response bodies for HTTP error traces, and MobileRequestError events.
NewRelic.httpResponseBodyCaptureEnabled(true);
Shut down the agent within the current application lifecycle during runtime.
NewRelic.shutdown();
This API allows you to add any header field strings to a list that gets recorded as attributes with networking request events. After header fields have been added using this function, if the headers are in a network call they will be included in networking events in NR1.
NewRelic.addHTTPHeadersTrackingFor(["Car","Music"]);
Sets the maximum size of total data that can be stored for offline storage.By default, mobile monitoring can collect a maximum of 100 megaBytes of offline storage. When a data payload fails to send because the device doesn't have an internet connection, it can be stored in the file system until an internet connection has been made. After a typical harvest payload has been successfully sent, all offline data is sent to New Relic and cleared from storage.
NewRelic.setMaxOfflineStorageSize(200);
logInfo(String message) : void
Logs an informational message to the New Relic log.
NewRelic.logInfo();
logError(String message) : void
Logs an error message to the New Relic log.
NewRelic.logError("This is an error message");
logVerbose(String message) : void
Logs a verbose message to the New Relic log.
NewRelic.logVerbose("This is a verbose message");
logWarning(String message) : void
Logs a warning message to the New Relic log.
NewRelic.logWarning("This is a warning message");
logDebug(String message) : void
Logs a debug message to the New Relic log.
NewRelic.logDebug("This is a debug message");
log(LogLevel level, String message) : void
Logs a message to the New Relic log with a specified log level.
NewRelic.log(LogLevel.INFO, "This is an informational message");
logAll(Error error,attributes?: {[key: string]: any}) : void
Logs an exception with attributes to the New Relic log.
Newrelic.logAll(new Error("This is an exception"),
{"BreadNumValue": 12.3 ,
"BreadStrValue": "FlutterBread",
"BreadBoolValue": true ,
"message": "This is a message with attributes" }
);
logAttributes(attributes?: {[key: string]: any}) : void
Logs a message with attributes to the New Relic log.
Newrelic.logAttributes(
{"BreadNumValue": 12.3 ,
"BreadStrValue": "FlutterBread",
"BreadBoolValue": true ,
"message": "This is a message with attributes",
level:newRelic.LogLevel.INFO });
How to see JSErrors(Fatal/Non Fatal) in NewRelic One?
React Native Agent v1.2.0 and above:
JavaScript errors and promise rejections can be seen in the Handled Exceptions tab in New Relic One. You will be able to see the event trail, attributes, and stack trace for each JavaScript error recorded.
You can also build a dashboard for these errors using this query:
SELECT * FROM MobileHandledException SINCE 24 hours ago
React Native Agent v1.1.0 and below:
There is no section for JavaScript errors, but you can see JavaScript errors in custom events and also query them in NRQL explorer.
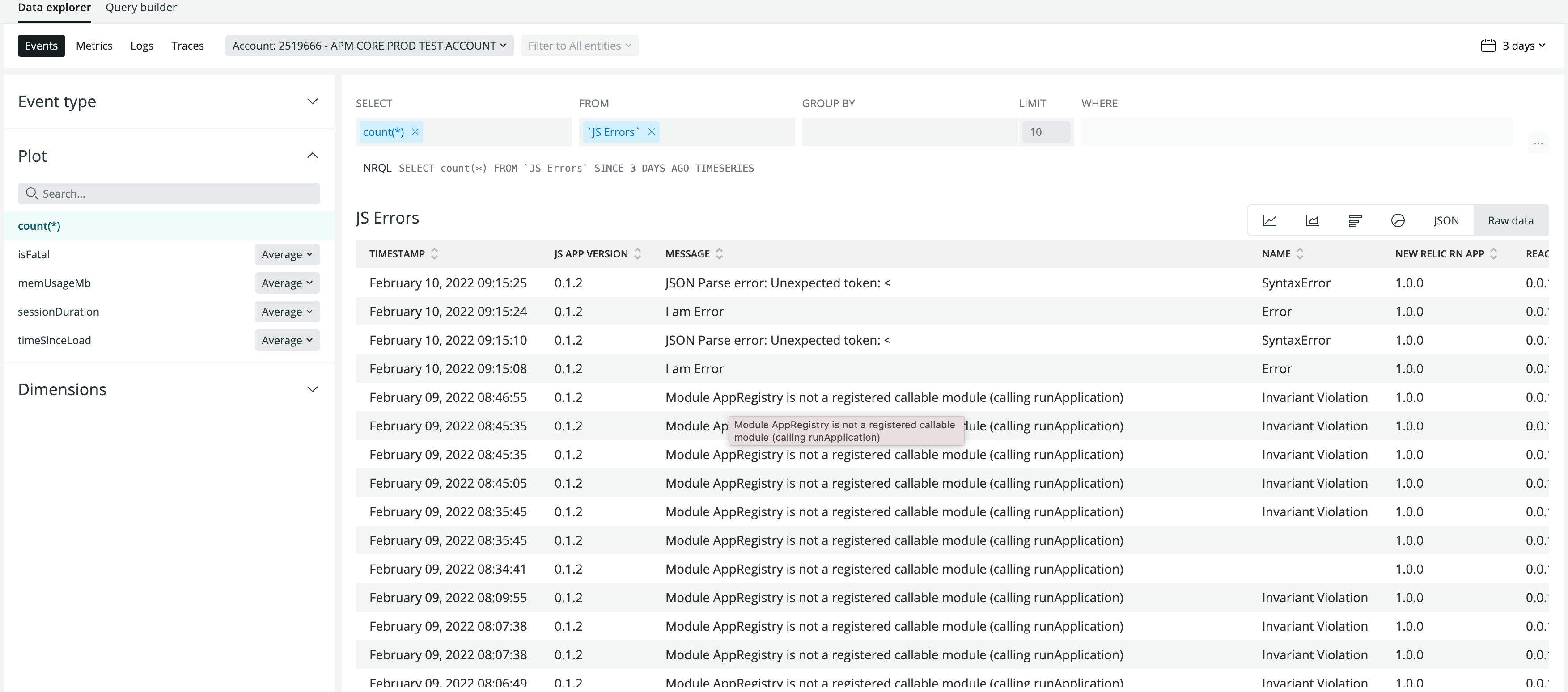
You can also build dashboard for errors using this query:
SELECT jsAppVersion,name,Message,errorStack,isFatal FROM `JS Errors` SINCE 24 hours ago
Symbolicating a stack trace
The agent supports symbolication of JavaScript errors in debug mode only. Symbolicated errors are shown as Handled Exceptions in New Relic One. If you want to manually symboliate, please follow the steps described here for Symbolication.
Symbolication for Javascript errors are coming in future releases.
* IMPORTANT considerations and best practices include:
*
* - You should limit the total number of event types to approximately five.
* eventType is meant to be used for high-level categories.
* For example, you might create an event type Gestures.
*
* - Do not use eventType to name your custom events.
* Create an attribute to name an event or use the optional name parameter.
* You can create many custom events; it is only event types that you should limit.
*
* - Using the optional name parameter has the same effect as adding a name key in the attributes dictionary.
* name is a keyword used for displaying your events in the New Relic UI.
* To create a useful name, you might combine several attributes.
Uploading dSYM files
Our iOS agent includes a Swift script intended to be run from a build script in your target's build phases in XCode. The script automatically uploads dSYM files in the background (or converts your dSYM to the New Relic map file format), and then performs a background upload of the files needed for crash symbolication to New Relic.
To invoke this script during an XCode build:
- Copy the dsym-upload-tools folder from this repository: https://github.com/newrelic/newrelic-ios-agent-spm, to your projects SRCROOT folder first.
- In Xcode, select your project in the navigator, then click on the application target.
- Select the Build Phases tab in the settings editor.
- Click the + icon above Target Dependencies and choose New Run Script Build Phase. Ensure the new build script is the very last build script.
- Add the following lines of code to the new phase and replace
APP_TOKEN with your iOS application token.
- If there is a checkbox below Run script that says "Run script: Based on Dependency analysis" please make sure it is not checked.
React Native agent 1.3.1 or higher
With the ios agent 7.4.6 release, the XCFramework no longer includes the dsym-upload-tools. You can find the dsym-upload-tools in the dsym-upload-tools folder of the https://github.com/newrelic/newrelic-ios-agent-spm Swift Package Manager repository. Please copy the dsym-upload-tools directory into your application source code directory by copying the XCFramework into your project or using Cocoapods if you're integrating the New Relic iOS Agent. Use the run script below in your Xcode build phases to perform symbol upload steps during app builds in Xcode.
ARTIFACT_DIR="${BUILD_DIR%Build/*}"
SCRIPT=`/usr/bin/find "${SRCROOT}" "${ARTIFACT_DIR}" -type f -name run-symbol-tool | head -n 1`
/bin/sh "${SCRIPT}" "APP_TOKEN"
React Native agent 0.0.8 or higher
ARTIFACT_DIR="${BUILD_DIR%Build/*}"
SCRIPT=`/usr/bin/find "${SRCROOT}" "${ARTIFACT_DIR}" -type f -name run-symbol-tool | head -n 1`
/bin/sh "${SCRIPT}" "APP_TOKEN"
React Native agent 0.0.7 or lower
SCRIPT=`/usr/bin/find "${SRCROOT}" -name newrelic_postbuild.sh | head -n 1`
if [ -z "${SCRIPT}"]; then
ARTIFACT_DIR="${BUILD_DIR%Build/*}SourcePackages/artifacts"
SCRIPT=`/usr/bin/find "${ARTIFACT_DIR}" -name newrelic_postbuild.sh | head -n 1`
fi
/bin/sh "${SCRIPT}" "APP_TOKEN"
Note: The automatic script requires bitcode to be disabled. You should clean and rebuild your app after adding the script.
Missing dSYMs
The automatic script will create an upload_dsym_results.log file in your project's iOS directory, which contains information about any failures that occur during symbol upload.
If dSYM files are missing, you may need to check Xcode build settings to ensure the file is being generated. Frameworks which are built locally have separate build settings and may need to be updated as well.
Build settings:
Debug Information Format : Dwarf with dSYM File
Deployment Postprocessing: Yes
Strip Linked Product: Yes
Strip Debug Symbols During Copy : Yes
Configure app launch times
To measure app launch time, you can refer to the following documentation for both Android and iOS platforms.
Testing
Jest Configuration
By default, node_modules are ignored by transformers by Jest. To configure the newrelic-react-native-agent to work with Jest, you should add this package to transformIgnorePatterns. We also provide some basic mocks for our API calls in jestSetup.js. Simply add this file to setupFiles in your Jest configuration. An example jest configuration would look like:
"jest": {
"preset": "react-native",
"transformIgnorePatterns": [
"node_modules/(?!@react-native|react-native|newrelic-react-native-agent)"
],
"setupFiles": [
"./node_modules/newrelic-react-native-agent/jestSetup.js"
]
}






