
Research
Security News
Quasar RAT Disguised as an npm Package for Detecting Vulnerabilities in Ethereum Smart Contracts
Socket researchers uncover a malicious npm package posing as a tool for detecting vulnerabilities in Etherium smart contracts.
A JavaScript lib to estimate scale, rotation, and translation between two sets of 2D points. Applicable for example in cases where one wants to move objects by multiple fingers or where a large number of points from an eye tracker device are wanted to be corrected based on a few calibration points. In general, you can apply nudged in any situation where you want to move a number of points based on a few sample points and optionally a fixed pivot point.
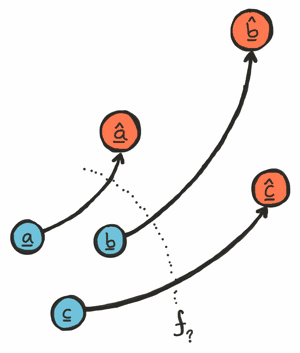
Mathematically speaking, nudged is an optimal least squares estimator for affine transformation matrices with uniform scaling, rotation, and translation and without reflection or shearing. The estimation has time complexity of O(n) that consists of 6n+22 multiplications and 11n+19 additions, where n is the cardinality (size) of the point sets. Under the constraint of a fixed pivot point, the number of operations is even smaller. In other words, nudged solves an affine 2D to 2D point set registration problem in linear time.
The development of nudged has been supported by Infant Cognition Laboratory at University of Tampere where it is used to correct eye tracking data.
Available also in Python.
To get a grip on how the transformation looks and how the points affect it, play with the interactive example app.

$ npm install nudged
Let domain and range be point sets before and after transformation i.e. the training data:
var domain = [[0,0], [2,0], [ 1,2]];
var range = [[1,1], [1,3], [-1,2]];
Compute an optimal transformation based on the points:
var trans = nudged.estimate(domain, range);
Alternatively, set a fixed pivot point that should not be altered in the transformation. You can think it as a pin or anchor:
var pivot = [3,3];
var pivotedTrans = nudged.estimateFixed(domain, range, pivot);
Examine the transformation matrix:
trans.getMatrix()
-> [[0,-1, 1],
[1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1]]
trans.getRotation()
-> 1.5707... = π / 2
trans.getScale()
-> 1.0
trans.getTranslation()
-> [1, 1]
Apply the transformation to other points:
trans.transform([2,2])
-> [-1,3]
Inverse the transformation:
var inv = trans.getInverse();
inv.transform([-1,3])
-> [2,2]
Compute an optimal affine transformation from the domain to range points.
Parameters
The domain and range should have equal length. Different lengths are allowed but additional points in the longer array are ignored in the estimation.
Return new nudged.Transform(...) instance.
Often one point, e.g. a corner of a picture, needs to stay put regardless of the domain and range.
Parameters
The domain and range should have equal length. Different lengths are allowed but additional points in the longer array are ignored in the estimation.
Return new nudged.Transform(...) instance.
Contains the module version string equal to the version in package.json.
An instance returned by the nudged.estimate(...).
In addition to the methods below, it has properties s, r, tx, ty that define the augmented transformation matrix:
|s -r tx|
|r s ty|
|0 0 1|
Apply the transform to a point or an array of points.
Return an array of transformed points or single point if only a point was given. For example:
trans.transform([1,1]) // [2,2]
trans.transform([[1,1]]) // [[2,2]]
trans.transform([[1,1], [2,3]]) // [[2,2], [3,4]]
Return an 3x3 augmented transformation matrix in the following array format:
[[s,-r, tx],
[r, s, ty],
[0, 0, 1]]
Get clockwise rotation from the positive x-axis.
Return rotation in radians.
Return scaling multiplier, e.g. 0.333 for a threefold shrink.
Return [tx, ty] where tx and ty denotes movement along x-axis and y-axis accordingly.
Return a new nudged.Transform instance that is the inverse of the transformation.
Throw an Error instance if the transformation is singular and cannot be inversed. This occurs if the range points are all the same which forces the scale to drop to zero.
Run lint & unit tests:
$ npm run test
Build example app:
$ npm run build:example
[0.4.0] - 2015-10-27
estimateFixed.nudged.estimate regarding single point pairs.FAQs
Affine transformation estimator e.g. for multi-touch gestures and calibration
The npm package nudged receives a total of 109 weekly downloads. As such, nudged popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that nudged demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 0 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers uncover a malicious npm package posing as a tool for detecting vulnerabilities in Etherium smart contracts.

Security News
Research
A supply chain attack on Rspack's npm packages injected cryptomining malware, potentially impacting thousands of developers.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers discovered a malware campaign on npm delivering the Skuld infostealer via typosquatted packages, exposing sensitive data.