opencv4nodejs-prebuilt-install




Simple installation Opencv 4.1.1 for node with pre-compiled bindings
Cross-platform!
Supports
- Windows, Linux , MacOS
- node 12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19
- arh x64
How to install
npm i opencv4nodejs-prebuilt-install
Examples
See examples for implementation.
Face Detection

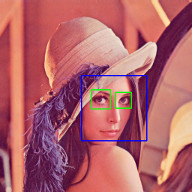
Face Recognition with the OpenCV face module
Check out Node.js + OpenCV for Face Recognition.

Face Landmarks with the OpenCV face module

Check out Node.js + face-recognition.js : Simple and Robust Face Recognition using Deep Learning.

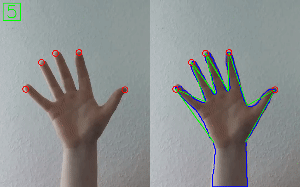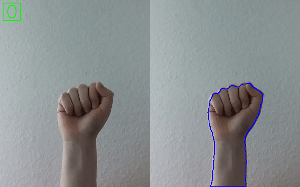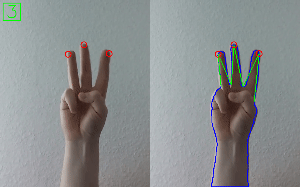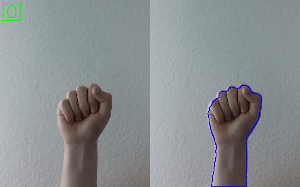
Hand Gesture Recognition
Check out Simple Hand Gesture Recognition using OpenCV and JavaScript.
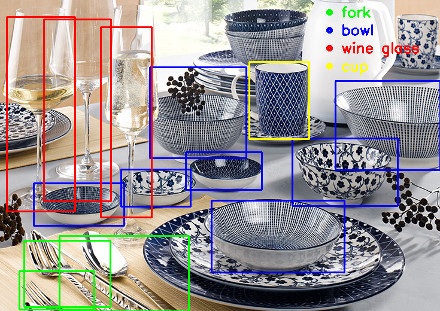
Object Recognition with Deep Neural Networks
Check out Node.js meets OpenCV’s Deep Neural Networks — Fun with Tensorflow and Caffe.
Tensorflow Inception



Single Shot Multibox Detector with COCO

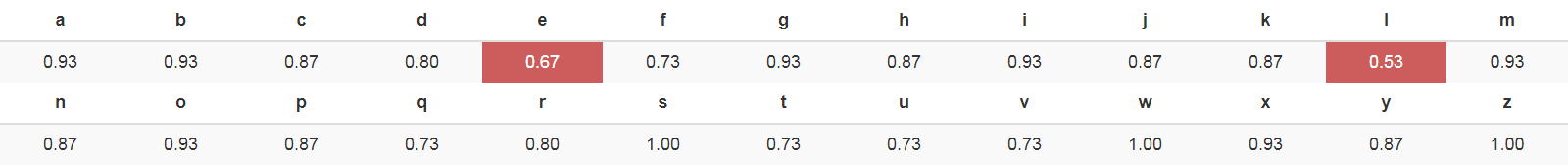
Machine Learning
Check out Machine Learning with OpenCV and JavaScript: Recognizing Handwritten Letters using HOG and SVM.
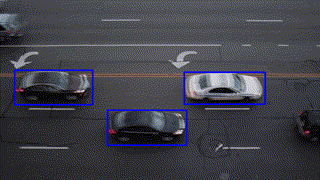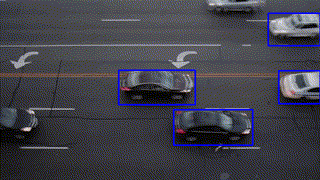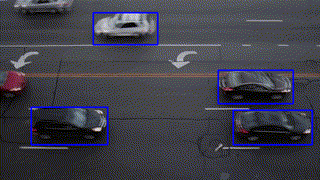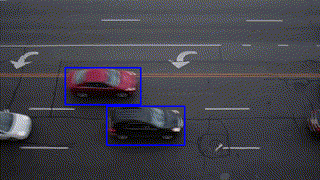
Object Tracking

Feature Matching

Image Histogram
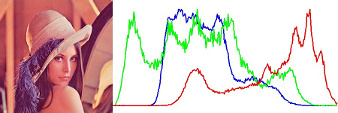
Boiler plate for combination of opencv4nodejs, express and websockets
opencv4nodejs-express-websockets - Boilerplate express app for getting started on opencv with nodejs and to live stream the video through websockets.
Automating lights by people detection through classifier
Check out Automating lights with Computer Vision & NodeJS.

Quick Start
const cv = require('opencv4nodejs-prebuilt-install');
Initializing Mat (image matrix), Vec, Point
const rows = 100;
const cols = 100;
const emptyMat = new cv.Mat(rows, cols, cv.CV_8UC3);
const whiteMat = new cv.Mat(rows, cols, cv.CV_8UC1, 255);
const blueMat = new cv.Mat(rows, cols, cv.CV_8UC3, [255, 0, 0]);
const matData = [
[[255, 0, 0], [255, 0, 0], [255, 0, 0]],
[[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]],
[[255, 0, 0], [255, 0, 0], [255, 0, 0]]
];
const matFromArray = new cv.Mat(matData, cv.CV_8UC3);
const charData = [255, 0, ...];
const matFromArray = new cv.Mat(Buffer.from(charData), rows, cols, cv.CV_8UC3);
const pt2 = new cv.Point(100, 100);
const pt3 = new cv.Point(100, 100, 0.5);
const vec2 = new cv.Vec(100, 100);
const vec3 = new cv.Vec(100, 100, 0.5);
const vec4 = new cv.Vec(100, 100, 0.5, 0.5);
Mat and Vec operations
const mat0 = new cv.Mat(...);
const mat1 = new cv.Mat(...);
const matMultipliedByScalar = mat0.mul(0.5);
const matDividedByScalar = mat0.div(2);
const mat0PlusMat1 = mat0.add(mat1);
const mat0MinusMat1 = mat0.sub(mat1);
const mat0MulMat1 = mat0.hMul(mat1);
const mat0DivMat1 = mat0.hDiv(mat1);
const mat0AndMat1 = mat0.and(mat1);
const mat0OrMat1 = mat0.or(mat1);
const mat0bwAndMat1 = mat0.bitwiseAnd(mat1);
const mat0bwOrMat1 = mat0.bitwiseOr(mat1);
const mat0bwXorMat1 = mat0.bitwiseXor(mat1);
const mat0bwNot = mat0.bitwiseNot();
Accessing Mat data
const matBGR = new cv.Mat(..., cv.CV_8UC3);
const matGray = new cv.Mat(..., cv.CV_8UC1);
const vec3 = matBGR.at(200, 100);
const grayVal = matGray.at(200, 100);
const [b, g, r] = matBGR.atRaw(200, 100);
matBGR.set(50, 50, [255, 0, 0]);
matBGR.set(50, 50, new Vec(255, 0, 0));
matGray.set(50, 50, 255);
const width = 25;
const height = 25;
const region = matBGR.getRegion(new cv.Rect(50, 50, width, height));
const matAsBuffer = matBGR.getData();
const matAsArray = matBGR.getDataAsArray();
IO
const mat = cv.imread('./path/img.jpg');
cv.imreadAsync('./path/img.jpg', (err, mat) => {
...
})
cv.imwrite('./path/img.png', mat);
cv.imwriteAsync('./path/img.jpg', mat, (err) => {
...
})
cv.imshow('a window name', mat);
cv.waitKey();
const base64text='data:image/png;base64,R0lGO..';
const base64data =base64text.replace('data:image/jpeg;base64','')
.replace('data:image/png;base64','');
const buffer = Buffer.from(base64data,'base64');
const image = cv.imdecode(buffer);
const outBase64 = cv.imencode('.jpg', croppedImage).toString('base64');
const htmlImg='<img src=data:image/jpeg;base64,'+outBase64 + '>';
const devicePort = 0;
const wCap = new cv.VideoCapture(devicePort);
const vCap = new cv.VideoCapture('./path/video.mp4');
const frame = vCap.read();
vCap.readAsync((err, frame) => {
...
});
const delay = 10;
let done = false;
while (!done) {
let frame = vCap.read();
if (frame.empty) {
vCap.reset();
frame = vCap.read();
}
const key = cv.waitKey(delay);
done = key !== 255;
}
Useful Mat methods
const matBGR = new cv.Mat(..., cv.CV_8UC3);
const matSignedInt = matBGR.convertTo(cv.CV_32SC3);
const matDoublePrecision = matBGR.convertTo(cv.CV_64FC3);
const matGray = matBGR.bgrToGray();
const matHSV = matBGR.cvtColor(cv.COLOR_BGR2HSV);
const matLab = matBGR.cvtColor(cv.COLOR_BGR2Lab);
const matHalfSize = matBGR.rescale(0.5);
const mat100x100 = matBGR.resize(100, 100);
const matMaxDimIs100 = matBGR.resizeToMax(100);
const [matB, matG, matR] = matBGR.splitChannels();
const matRGB = new cv.Mat([matR, matB, matG]);
Drawing a Mat into HTML Canvas
const img = ...
const matRGBA = img.channels === 1
? img.cvtColor(cv.COLOR_GRAY2RGBA)
: img.cvtColor(cv.COLOR_BGR2RGBA);
const imgData = new ImageData(
new Uint8ClampedArray(matRGBA.getData()),
img.cols,
img.rows
);
const canvas = document.getElementById('myCanvas');
canvas.height = img.rows;
canvas.width = img.cols;
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.putImageData(imgData, 0, 0);
Method Interface
OpenCV method interface from official docs or src:
void GaussianBlur(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, Size ksize, double sigmaX, double sigmaY = 0, int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT);
translates to:
const src = new cv.Mat(...);
const dst0 = src.gaussianBlur(new cv.Size(5, 5), 1.2);
const dst2 = src.gaussianBlur(new cv.Size(5, 5), 1.2, 0.8, cv.BORDER_REFLECT);
const optionalArgs = {
borderType: cv.BORDER_CONSTANT
};
const dst2 = src.gaussianBlur(new cv.Size(5, 5), 1.2, optionalArgs);
Async API
The async API can be consumed by passing a callback as the last argument of the function call. By default, if an async method is called without passing a callback, the function call will yield a Promise.
Async Face Detection
const classifier = new cv.CascadeClassifier(cv.HAAR_FRONTALFACE_ALT2);
cv.imreadAsync('./faceimg.jpg', (err, img) => {
if (err) { return console.error(err); }
const grayImg = img.bgrToGray();
classifier.detectMultiScaleAsync(grayImg, (err, res) => {
if (err) { return console.error(err); }
const { objects, numDetections } = res;
...
});
});
cv.imreadAsync('./faceimg.jpg')
.then(img =>
img.bgrToGrayAsync()
.then(grayImg => classifier.detectMultiScaleAsync(grayImg))
.then((res) => {
const { objects, numDetections } = res;
...
})
)
.catch(err => console.error(err));
try {
const img = await cv.imreadAsync('./faceimg.jpg');
const grayImg = await img.bgrToGrayAsync();
const { objects, numDetections } = await classifier.detectMultiScaleAsync(grayImg);
...
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
With TypeScript
import * as cv from 'opencv4nodejs-prebuilt-install'
Check out the TypeScript examples.
External Memory Tracking (v4.0.0)
Since version 4.0.0 was released, external memory tracking has been enabled by default. Simply put, the memory allocated for Matrices (cv.Mat) will be manually reported to the node process. This solves the issue of inconsistent Garbage Collection, which could have resulted in spiking memory usage of the node process eventually leading to overflowing the RAM of your system, prior to version 4.0.0.
Note, that in doubt this feature can be disabled by setting an environment variable OPENCV4NODEJS_DISABLE_EXTERNAL_MEM_TRACKING before requiring the module:
export OPENCV4NODEJS_DISABLE_EXTERNAL_MEM_TRACKING=1 // linux
set OPENCV4NODEJS_DISABLE_EXTERNAL_MEM_TRACKING=1 // windows
Or directly in your code:
process.env.OPENCV4NODEJS_DISABLE_EXTERNAL_MEM_TRACKING = 1
const cv = require('opencv4nodejs-prebuilt-install')























