opencv4nodejs





By its nature, JavaScript lacks the performance to implement Computer Vision tasks efficiently. Therefore this package brings the performance of the native OpenCV library to your Node.js application. Supports all OpenCV 3 versions. The bindings are available as an asynchronous (via promises or callbacks) and synchronous API.
The ultimate goal of this project is to provide a collection of Node.js bindings, which supports the entire OpenCV and OpenCV-contrib API. An overview of available bindings can be found in the API Documentation. The implementation of missing bindings can be specifically prioritized by requesting new features. Furthermore, contribution is highly appreciated. If you want to get involved you can have a look at the contribution guide.
Examples
See examples for implementation.
Face Detection

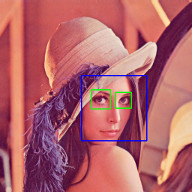
Face Recognition with the OpenCV face module
Check out Node.js + OpenCV for Face Recognition.

Check out Node.js + face-recognition.js : Simple and Robust Face Recognition using Deep Learning.

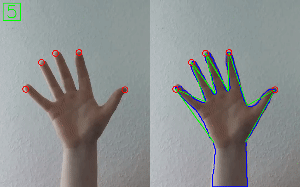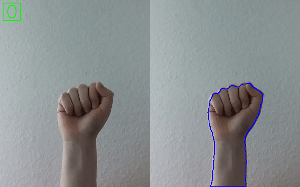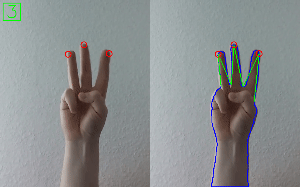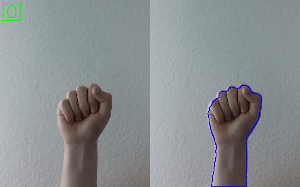
Hand Gesture Recognition
Check out Simple Hand Gesture Recognition using OpenCV and JavaScript.
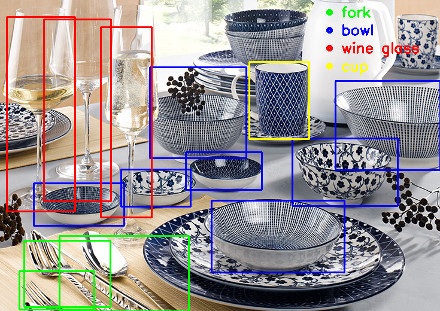
Object Recognition with Deep Neural Networks
Check out Node.js meets OpenCV’s Deep Neural Networks — Fun with Tensorflow and Caffe.
Tensorflow Inception



Single Shot Multibox Detector with COCO

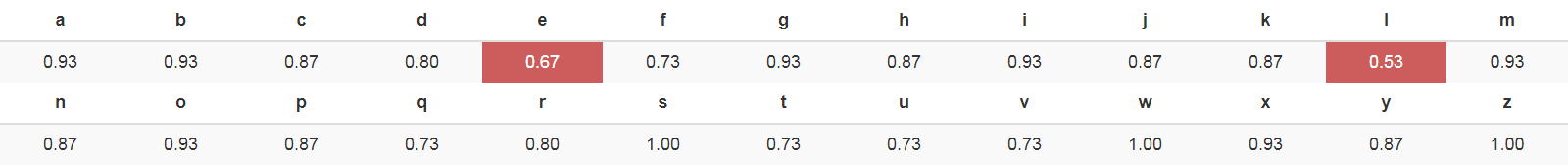
Machine Learning
Check out Machine Learning with OpenCV and JavaScript: Recognizing Handwritten Letters using HOG and SVM.
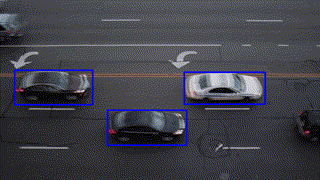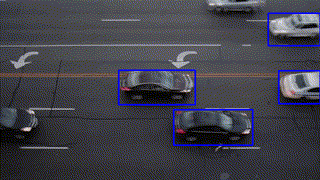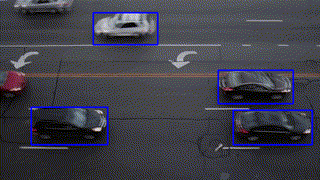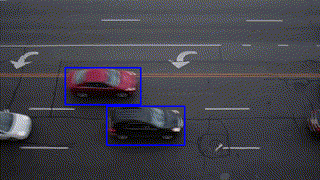
Object Tracking

Feature Matching

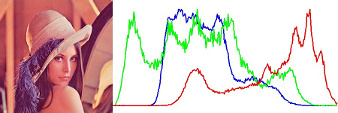
Image Histogram
How to install
Requirements
- cmake (unless you are using a prebuilt OpenCV release)
On Windows
On windows you will need Windows Build Tools to compile OpenCV and opencv4nodejs. If you don't have Visual Studio or Windows Build Tools installed, you can easily install the VS2015 build tools:
npm install --global windows-build-tools
Auto build
If you do not want to set up OpenCV on your own you can simply let this package auto install OpenCV 3.4 + OpenCV contrib 3.4 (might take some time):
$ npm install --save opencv4nodejs
Manual build
Setting up OpenCV on your own will require you to set an environment variable: OPENCV4NODEJS_DISABLE_AUTOBUILD=1.
You can either install any of the OpenCV 3+ releases (note, this will come without contrib) or build OpenCV with or without OpenCV contrib from source on your own. On Linux and MacOSX the library should be installed under usr/local (which is the default).
On Windows
If you choose to set up OpenCV on your own you have to set the following environment variables before installing opencv4nodejs:
- OPENCV_INCLUDE_DIR pointing to the directory with the subfolders opencv and opencv2 containing the header files
- OPENCV_LIB_DIR pointing to the lib directory containing the OpenCV .lib files
Also you will need to add the OpenCV binaries to your system path:
- add an environment variable OPENCV_BIN_DIR pointing to the binary directory containing the OpenCV .dll files
- append
;%OPENCV_BIN_DIR%; to your system path variable
Note: Restart your current console session after making changes to your environment.
If you are running into issues also check the requirements for node-gyp specific to your OS: https://github.com/nodejs/node-gyp.
Usage with Docker
opencv-express - example for opencv4nodejs with express.js and docker
Or simply pull from justadudewhohacks/opencv-nodejs for opencv-3.2 + contrib-3.2 with opencv4nodejs globally installed:
FROM justadudewhohacks/opencv-nodejs
Different OpenCV 3.x base images can be found here: https://hub.docker.com/r/justadudewhohacks/.
Usage with Electron
opencv-electron - example for opencv4nodejs with electron
Add the following script to your package.json:
"electron-rebuild": "electron-rebuild -w opencv4nodejs"
Run the script:
$ npm run electron-rebuild
Require it in the application:
const cv = require('opencv4nodejs');
Usage with NW.js
Any native modules, including opencv4nodejs, must be recompiled to be used with NW.js. Instructions on how to do this are available in the [Use Native Modules] (http://docs.nwjs.io/en/latest/For%20Users/Advanced/Use%20Native%20Node%20Modules/) section of the the NW.js documentation.
Once recompiled, the module can be installed and required as usual:
const cv = require('opencv4nodejs');
Quick Start
const cv = require('opencv4nodejs');
Initializing Mat (image matrix), Vec, Point
const rows = 100;
const cols = 100;
const emptyMat = new cv.Mat(rows, cols, cv.CV_8UC3);
const whiteMat = new cv.Mat(rows, cols, cv.CV_8UC1, 255);
const blueMat = new cv.Mat(rows, cols, cv.CV_8UC3, [255, 0, 0]);
const matData = [
[[255, 0, 0], [255, 0, 0], [255, 0, 0]],
[[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]],
[[255, 0, 0], [255, 0, 0], [255, 0, 0]]
];
const matFromArray = new cv.Mat(matData, cv.CV_8UC3);
const charData = [255, 0, ...];
const matFromArray = new cv.Mat(new Buffer.from(charData), rows, cols, cv.CV_8UC3);
const pt2 = new cv.Point(100, 100);
const pt3 = new cv.Point(100, 100, 0.5);
const vec2 = new cv.Vec(100, 100);
const vec3 = new cv.Vec(100, 100, 0.5);
const vec4 = new cv.Vec(100, 100, 0.5, 0.5);
Mat and Vec operations
const mat0 = new cv.Mat(...);
const mat1 = new cv.Mat(...);
const matMultipliedByScalar = mat0.mul(0.5);
const matDividedByScalar = mat0.div(2);
const mat0PlusMat1 = mat0.add(mat1);
const mat0MinusMat1 = mat0.sub(mat1);
const mat0MulMat1 = mat0.hMul(mat1);
const mat0DivMat1 = mat0.hDiv(mat1);
const mat0AndMat1 = mat0.and(mat1);
const mat0OrMat1 = mat0.or(mat1);
const mat0bwAndMat1 = mat0.bitwiseAnd(mat1);
const mat0bwOrMat1 = mat0.bitwiseOr(mat1);
const mat0bwXorMat1 = mat0.bitwiseXor(mat1);
const mat0bwNot = mat0.bitwiseNot();
Accessing Mat data
const matBGR = new cv.Mat(..., cv.CV_8UC3);
const matGray = new cv.Mat(..., cv.CV_8UC1);
const vec3 = matBGR.at(200, 100);
const grayVal = matGray.at(200, 100);
const [b, g, r] = matBGR.atRaw(200, 100);
matBGR.set(50, 50, [255, 0, 0]);
matBGR.set(50, 50, new Vec(255, 0, 0));
matGray.set(50, 50, 255);
const width = 25;
const height = 25;
const region = matBGR.getRegion(new cv.Rect(50, 50, width, height));
const matAsBuffer = matBGR.getData();
const matAsArray = matBGR.getDataAsArray();
IO
const mat = cv.imread('./path/img.jpg');
cv.imreadAsync('./path/img.jpg', (err, mat) => {
...
})
cv.imwrite('./path/img.png', mat);
cv.imwriteAsync('./path/img.jpg', mat,(err) => {
...
})
cv.imshow('a window name', mat);
cv.waitKey();
const base64text='data:image/png;base64,R0lGO..';
const base64data =base64text.replace('data:image/jpeg;base64','')
.replace('data:image/png;base64','');
const buffer = Buffer.from(base64data,'base64');
const image = cv.imdecode(buffer);
const outBase64 = cv.imencode('.jpg', croppedImage).toString('base64');
const htmlImg='<img src=data:image/jpeg;base64,'+outBase64 + '>';
const devicePort = 0;
const wCap = new cv.VideoCapture(devicePort);
const vCap = new cv.VideoCapture('./path/video.mp4');
const frame = vCap.read();
vCap.readAsync((err, frame) => {
...
});
const delay = 10;
let done = false;
while (!done) {
let frame = vCap.read();
if (frame.empty) {
vCap.reset();
frame = vCap.read();
}
const key = cv.waitKey(delay);
done = key !== 255;
}
Useful Mat methods
const matBGR = new cv.Mat(..., cv.CV_8UC3);
const matSignedInt = matBGR.convertTo(cv.CV_32SC3);
const matDoublePrecision = matBGR.convertTo(cv.CV_64FC3);
const matGray = matBGR.bgrToGray();
const matHSV = matBGR.cvtColor(cv.COLOR_BGR2HSV);
const matLab = matBGR.cvtColor(cv.COLOR_BGR2Lab);
const matHalfSize = matBGR.rescale(0.5);
const mat100x100 = matBGR.resize(100, 100);
const matMaxDimIs100 = matBGR.resizeToMax(100);
const [matB, matG, matR] = matBGR.splitChannels();
const matRGB = new cv.Mat([matR, matB, matG]);
Drawing a Mat into HTML Canvas
const img = ...
const matRGBA = img.channels === 1
? img.cvtColor(cv.COLOR_GRAY2RGBA)
: img.cvtColor(cv.COLOR_BGR2RGBA);
const imgData = new ImageData(
new Uint8ClampedArray(matRGBA.getData()),
img.cols,
img.rows
);
const canvas = document.getElementById('myCanvas');
canvas.height = img.rows;
canvas.width = img.cols;
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.putImageData(imgData, 0, 0);
Method Interface
OpenCV method interface from official docs or src:
void GaussianBlur(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, Size ksize, double sigmaX, double sigmaY = 0, int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT);
translates to:
const src = new cv.Mat(...);
const dst0 = src.gaussianBlur(new cv.Size(5, 5), 1.2);
const dst2 = src.gaussianBlur(new cv.Size(5, 5), 1.2, 0.8, cv.BORDER_REFLECT);
const optionalArgs = {
borderType: cv.BORDER_CONSTANT
};
const dst2 = src.gaussianBlur(new cv.Size(5, 5), 1.2, optionalArgs);
Async API
The async API can be consumed by passing a callback as the last argument of the function call. By default, if an async method is called without passing a callback, the function call will yield a Promise.
Async Face Detection
const classifier = new cv.CascadeClassifier(cv.HAAR_FRONTALFACE_ALT2);
cv.imreadAsync('./faceimg.jpg', (err, img) => {
if (err) { return console.error(err); }
const grayImg = img.bgrToGray();
classifier.detectMultiScaleAsync(grayImg, (err, res) => {
if (err) { return console.error(err); }
const { objects, numDetections } = res;
...
});
});
cv.imreadAsync('./faceimg.jpg')
.then(img =>
img.bgrToGrayAsync()
.then(grayImg => classifier.detectMultiScaleAsync(grayImg))
.then((res) => {
const { objects, numDetections } = res;
...
})
)
.catch(err => console.error(err));
try {
const img = await cv.imreadAsync('./faceimg.jpg');
const grayImg = await img.bgrToGrayAsync();
const { objects, numDetections } = await classifier.detectMultiScaleAsync(grayImg);
...
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
Available Modules
Request new Features
Are you missing some functions from OpenCV (overview of available bindings) or have an idea for utility in regards to the OpenCV API, which you would like to be added to this package? No problem! Open a new issue with a listing of the desired function bindings or features and you will find them in this package soon.





















