


RxSandbox
RxSandbox is test suite for RxJS, based on marble diagram DSL for easier assertion around Observables.
For RxJS 5 support, check pre-1.x versions. 1.x supports latest RxJS 6.x.
What's difference with TestScheduler in RxJS?
RxJS 5's test cases are written via its own TestScheduler implementation. While it still can be used for testing any other Observable based codes its ergonomics are not user code friendly, reason why core repo tracks issue to provide separate package for general usage. RxSandbox aims to resolve those ergonomics with few design goals
- Provides feature parity to
TestScheduler - Support extended marble diagram DSL
- Near-zero configuration, works out of box
- No dependencies to specific test framework
Install
This has a peer dependencies of rxjs@5.*.*, which will have to be installed as well
npm install rx-sandbox
Usage
Observable marble diagram token description
In RxSandbox, Observable is represented via marble diagram. Marble syntax is a string represents events happening over virtual time so called as frame.
- : Single frame of time passage, by default 1.| : Successful completion of an observable signaling complete().# : An error terminating the observable signaling error(). (whitespace) : Noop, whitespace does nothing but allows align marbles for readability.a : Any other character than predefined token represents a value being emitted by next()() : When multiple events need to single in the same frame synchronously, parenthesis are used to group those events. You can group nexted values, a completion or an error in this manner. The position of the initial (determines the time at which its values are emitted.^ : (hot observables only) Shows the point at which the tested observables will be subscribed to the hot observable. This is the "zero frame" for that observable, every frame before the ^ will be negative.! : (for subscription testing) Shows the point at which the tested observables will be unsubscribed....n... : (n is number) Expanding timeframe. For cases of testing long time period in observable, can shorten marble diagram instead of repeating -.
The first character of marble string always represents 0 frame.
Few examples
const never = `------`;
const empty = `|`;
const error = `#`;
const obs1 = `----a----`;
const obs2 = `----a---|`;
const obs2 = `-a-^-b--|`;
const obs3 = `--(abc)-|`;
const obs4 = `----(a|)`;
const obs5 = ` - --a- -|`;
const obs6 = `--...4...--|`
Subscription marble diagram token description
The subscription marble syntax is slightly different to conventional marble syntax. It represents the subscription and an unsubscription points happening over time. There should be no other type of event represented in such diagram.
- : Single frame of time passage, by default 1.^ : Shows the point in time at which a subscription happen.! : Shows the point in time at which a subscription is unsubscribed.- (whitespace) : Noop, whitespace does nothing but allows align marbles for readability.
...n... : (n is number) Expanding timeframe. For cases of testing long time period in observable, can shorten marble diagram instead of repeating -.
There should be at most one ^ point in a subscription marble diagram, and at most one ! point. Other than that, the - character is the only one allowed in a subscription marble diagram.
Few examples
const sub1 = `-----`;
const sub2 = `--^--`;
const sub3 = `--^--!-`;
Anatomy of test interface
You can import rxSandbox, and create instance using create().
import { expect } from 'chai';
import { rxSandbox } from 'rx-sandbox';
it('testcase', () => {
const { hot, cold, flush, getMessages, e, s } = rxSandbox.create();
const e1 = hot(' --^--a--b--|');
const e2 = cold(' ---x--y--|', {x: 1, y: 2});
const expected = e(' ---q--r--|');
const sub = s(' ^ !');
const messages = getMessages(e1.merge(e2));
flush();
expect(messages).to.deep.equal(expected);
expect(e1.subscriptions).to.deep.equal(sub);
});
Creating sandbox
rxSandbox.create(autoFlush?: boolean, frameTimeFactor?: number): RxSandboxInstance
Optional parameter values will be described further.
Using RxSandboxInstance
RxSandboxInstance exposes below interfaces.
Creating hot, cold observable
hot<T = string>(marble: string, value?: { [key: string]: T } | null, error?: any): HotObservable<T>;
hot<T = string>(messages: Array<TestMessage<T>>): HotObservable<T>;
cold<T = string>(marble: string, value?: { [key: string]: T } | null, error?: any): ColdObservable<T>;
cold<T = string>(messages: Array<TestMessage<T>>): ColdObservable<T>;
Both interfaces accepts marble diagram string, and optionally accepts custom values for marble values or errors. Otherwise, you can create Array<TestMessage<T>> directly instead of marble diagram.
Creating expected value, subscriptions
To compare observable's result, we can use marble diagram as well wrapped by utility function to generate values to be asserted.
e<T = string>(marble: string, value?: { [key: string]: T } | null, error?: any): Array<TestMessage<T>>;
It accepts same parameter to hot / cold observable creation but instead of returning observable, returns array of metadata for marble diagram.
Subscription metadata also need to be generated via wrapped function.
s(marble: string): SubscriptionLog;
Getting values from observable
Once we have hot, cold observables we can get metadata from those observables as well to assert with expected metadata values.
getMessages<T = string>(observable: Observable<any>, unsubscriptionMarbls: string = null): Array<TestMessage<T>>>;
const e1 = hot('--a--b--|');
const messages = getMessages(e1.mapTo('x'));
assert(messages.length === 0);
It is important to note at the moment of getting metadata array, it is not filled with actual value but just empty array. Scheduler should be flushed to fill in values.
const e1 = hot(' --a--b--|');
const expected = e('--x--x--|')
const subs = s(` ^ !`);
const messages = getMessages(e1.mapTo('x'));
expect(messages).to.be.empty;
flush();
expect(messages).to.deep.equal(expected);
expect(e1.subscriptions).to.deep.equal(subs);
Or if you need to control timeframe instead of flush out whole at once, you can use advanceTo as well.
const e1 = hot(' --a--b--|');
const subs = s(` ^ !`);
const messages = getMessages(e1.mapTo('x'));
expect(messages).to.be.empty;
advanceTo(3);
const expected = e('--x------');
expect(messages).to.deep.equal(expected);
expect(e1.subscriptions).to.deep.equal(subs);
Flushing scheduler automatically
By default sandbox instance requires to flush() explicitly to execute observables. For cases each test case doesn't require to schedule multiple observables but only need to test single, we can create sandbox instance to flush automatically. Since it flushes scheduler as soon as getMessages being called, subsequent getMessages call will raise errors.
const { hot, e } = rxSandbox.create(true);
const e1 = hot(' --a--b--|');
const expected = e('--x--x--|')
const messages = getMessages(e1.mapTo('x'));
expect(messages).to.deep.equal(expected);
expect(() => getMessages(e1.mapTo('y'))).to.throw();
Custom frame time factor
Each timeframe - is predefined to 1, can be overridden.
const { e } = rxSandbox.create(false, 10);
const expected = e('--x--x--|');
expect(expected[0].frame).to.equal(20);
Custom assertion for marble diagram
Messages generated by rxSandbox is plain object array, so any kind of assertion can be used. In addition to those, rxSandbox provides own custom assertion method marbleAssert for easier marble diagram diff.
marbleAssert<T = string>(source: Array<SubscriptionLog | TestMessage<T>>): { to: { equal(expected: Array<SubscriptionLog | TestMessage<T>>): void } }
It accepts array of test messages generated by getMessages and e, or subscription log by Hot/ColdObservable.subscriptions or s (in case of utility method s it returns single subscription, so need to be constructed as array).
import { rxSandbox } from 'rx-sandbox';
const { marbleAssert } = rxSandbox;
const {hot, e, s, getMessages, flush} = rxSandbox.create();
const source = hot('---a--b--|');
const expected = e('---x--x---|');
const sub = s('^-----!');
const messages = getMessages(source.mapTo('x'));
flush();
marbleAssert(messages).to.equal(expected);
marbleAssert(source.subscriptions).to.equal([sub]);
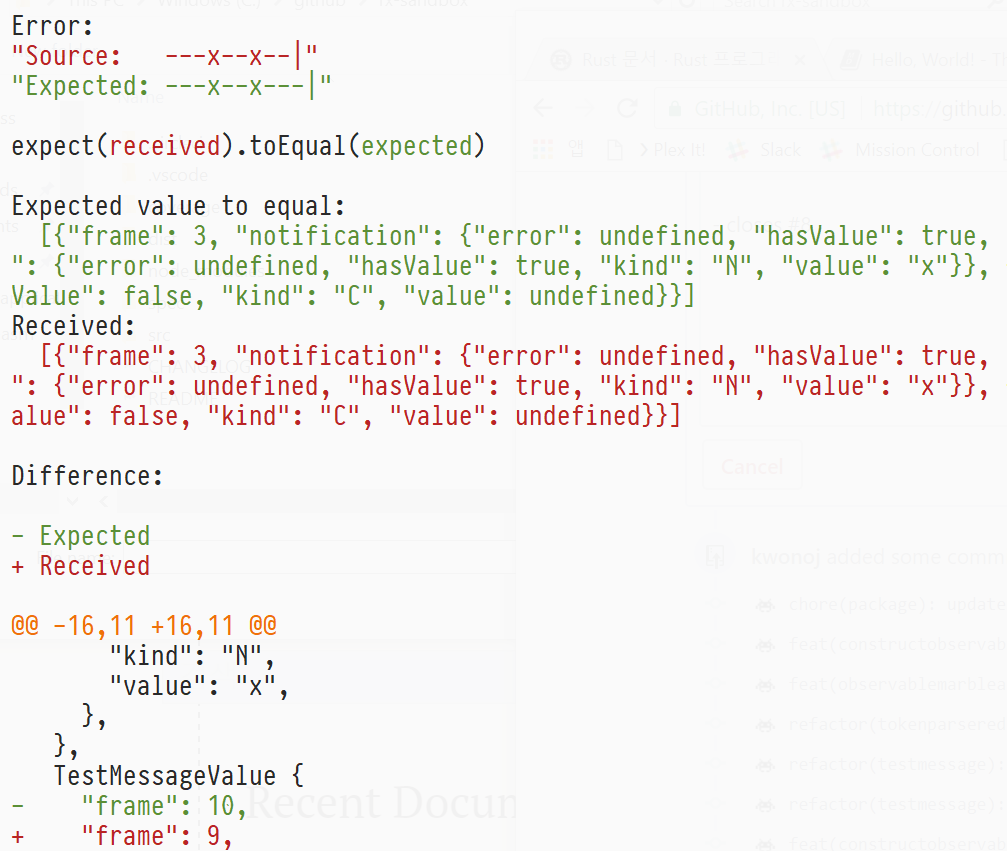
When assertion fails, it'll display visual / object diff with raw object values for easier debugging.
Assert Observable marble diagram
Assert subscription log marble diagram

Building / Testing
Few npm scripts are supported for build / test code.
build: Transpiles code to ES5 commonjs to dist.build:clean: Clean up existing buildtest: Run unit test. Does not require build before execute test.lint: Run lint over all codebaseslint:staged: Run lint only for staged changes. This'll be executed automatically with precommit hook.commit: Commit wizard to write commit message






