



VoxelCity
VoxelCity is a Python package that facilitates the creation of voxel-based 3D urban environments and related geospatial analyses. It integrates various geospatial datasets—such as building footprints, land cover, canopy height, and digital elevation models (DEMs)—to generate 2D and 3D representations of urban areas. It can export data in formats compatible with popular simulation tools like ENVI-MET, as well as visualization tools like MagicaVoxel, and supports simulations such as sky view index and green view index calculations.
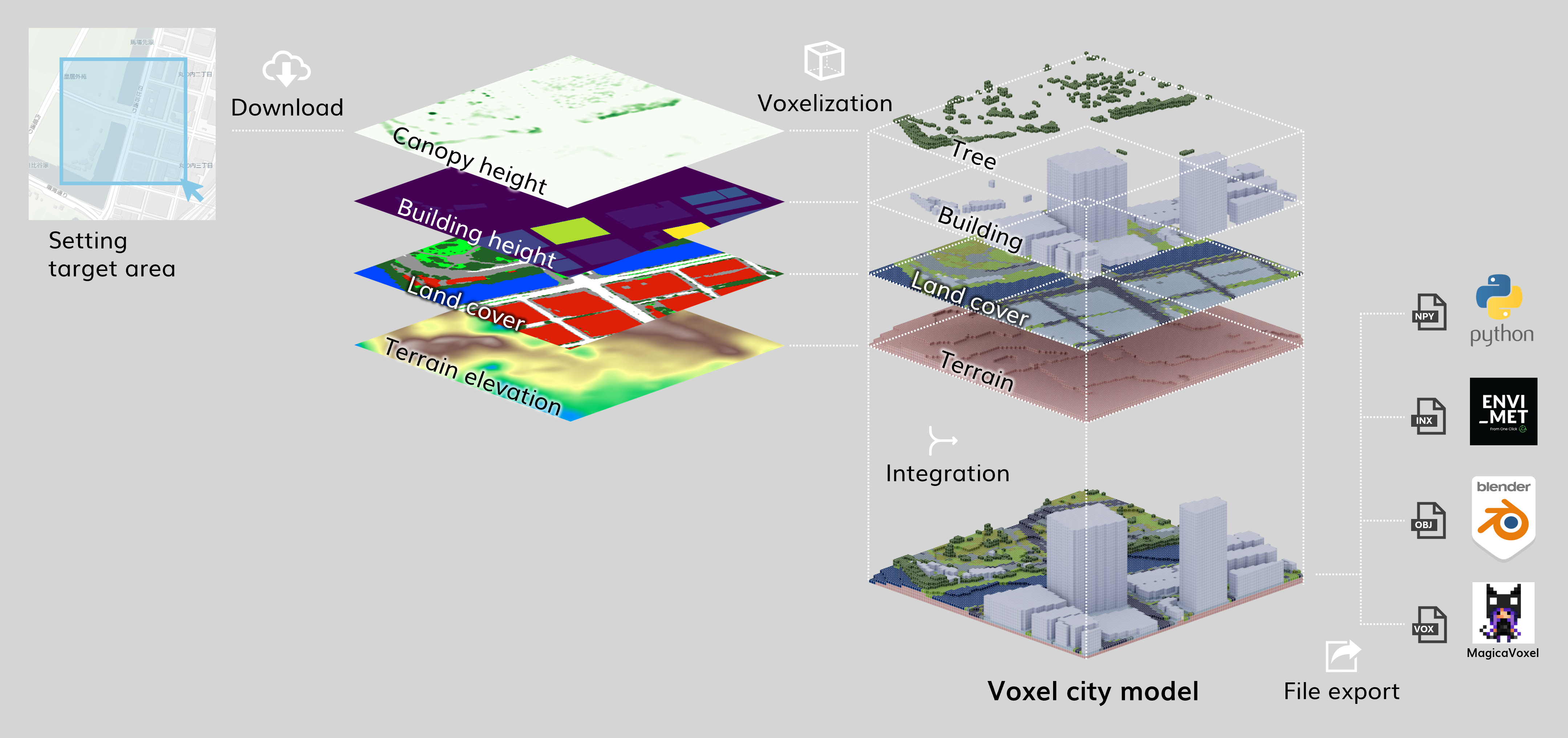
Key Features
-
Integration of Multiple Data Sources:
Combines building footprints, land cover data, canopy height maps, and DEMs to generate a consistent 3D voxel representation of an urban scene.
-
Flexible Input Sources:
Supports various building and terrain data sources including:
- Building Footprints: OpenStreetMap, Overture, EUBUCCO, Microsoft Building Footprints, OpenMapTiles, Open Building 2.5D
- Land Cover: UrbanWatch, OpenEarthMap Japan, ESA WorldCover, ESRI Land Cover, Dynamic World, OpenStreetMap
- Canopy Height: High Resolution 1m Global Canopy Height Maps, ETH Global Sentinel-2 10m
- DEM: DeltaDTM, FABDEM, NASA, COPERNICUS, and more
Detailed information about each data source can be found in the References of Data Sources section.
-
Customizable Domain and Resolution:
Easily define a target area by drawing a rectangle on a map or specifying center coordinates and dimensions. Adjust the mesh size to meet resolution needs.
-
Integration with Earth Engine:
Leverages Google Earth Engine for large-scale geospatial data processing (authentication and project setup required).
-
Output Formats:
- ENVI-MET: Export INX and EDB files suitable for ENVI-MET microclimate simulations.
- MagicaVoxel: Export vox files for 3D editing and visualization in MagicaVoxel.
- OBJ: Export wavefront OBJ for rendering and integration into other workflows.
-
Analytical Tools:
- View Index Simulations: Compute sky view index (SVI) and green view index (GVI) from a specified viewpoint.
- Landmark Visibility Maps: Assess the visibility of selected landmarks within the voxelized environment.
Installation
Make sure you have Python 3.12 installed. Install VoxelCity with:
For Local Environment
conda create --name voxelcity python=3.12
conda activate voxelcity
conda install -c conda-forge gdal
pip install voxelcity
For Google Colab
!pip install voxelcity
Setup for Earth Engine
To use Earth Engine data, set up your Earth Engine enabled Cloud Project by following the instructions here:
https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/cloud/earthengine_cloud_project_setup
After setting up, authenticate and initialize Earth Engine:
For Local Environment
earthengine authenticate
For Google Colab
!earthengine authenticate --auth_mode=notebook
Usage Overview
1. Authenticate Earth Engine
import ee
ee.Authenticate()
ee.Initialize(project='your-project-id')
2. Define Target Area
You can define your target area in three ways:
Option 1: Direct Coordinate Input
Define the target area by directly specifying the coordinates of the rectangle vertices.
rectangle_vertices = [
(47.59830044521263, -122.33587348582083),
(47.60279755390168, -122.33587348582083),
(47.60279755390168, -122.32922451417917),
(47.59830044521263, -122.32922451417917)
]
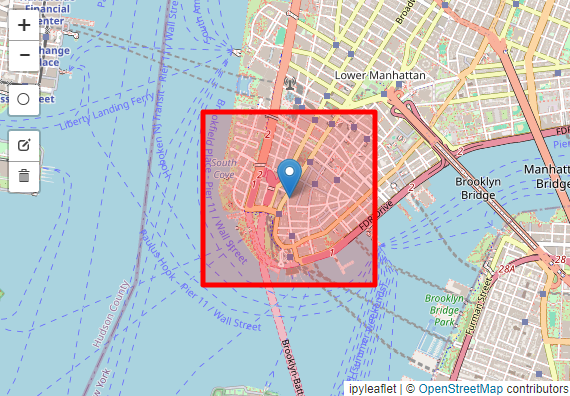
Option 2: Draw a Rectangle (for Jupyter Notebook)
Use the GUI map interface to draw a rectangular domain of interest.
from voxelcity.geo.draw import draw_rectangle_map_cityname
cityname = "tokyo"
m, rectangle_vertices = draw_rectangle_map_cityname(cityname, zoom=15)
m
Option 3: Specify Center and Dimensions (for Jupyter Notebook)
Choose the width and height in meters and select the center point on the map.
from voxelcity.geo.draw import center_location_map_cityname
width = 500
height = 500
m, rectangle_vertices = center_location_map_cityname(cityname, width, height, zoom=15)
m
3. Set Parameters
Define data sources and mesh size (m):
building_source = 'OpenStreetMap'
land_cover_source = 'OpenStreetMap'
canopy_height_source = 'High Resolution 1m Global Canopy Height Maps'
dem_source = 'DeltaDTM'
meshsize = 5
kwargs = {
"output_dir": "output",
"dem_interpolation": True
}
4. Get VoxelCity Output
Generate voxel data grids and corresponding building geoJSON:
from voxelcity import get_voxelcity
voxelcity_grid, building_height_grid, building_min_height_grid, \
building_id_grid, canopy_height_grid, land_cover_grid, dem_grid, \
building_geojson = get_voxelcity(
rectangle_vertices,
building_source,
land_cover_source,
canopy_height_source,
dem_source,
meshsize,
**kwargs
)
5. Exporting Files
ENVI-MET INX/EDB Files:
ENVI-MET is an advanced microclimate simulation software specialized in modeling urban environments. It simulates the interactions between buildings, vegetation, and various climate parameters like temperature, wind flow, humidity, and radiation. The software is used widely in urban planning, architecture, and environmental studies (Commercial, offers educational licenses).
from voxelcity.file.envimet import export_inx, generate_edb_file
envimet_kwargs = {
"output_directory": "output",
"author_name": "your name",
"model_description": "generated with VoxelCity",
"domain_building_max_height_ratio": 2,
"useTelescoping_grid": True,
"verticalStretch": 20,
"min_grids_Z": 20,
"lad": 1.0
}
export_inx(building_height_grid, building_id_grid, canopy_height_grid, land_cover_grid, dem_grid, meshsize, land_cover_source, rectangle_vertices, **envimet_kwargs)
generate_edb_file(**envimet_kwargs)
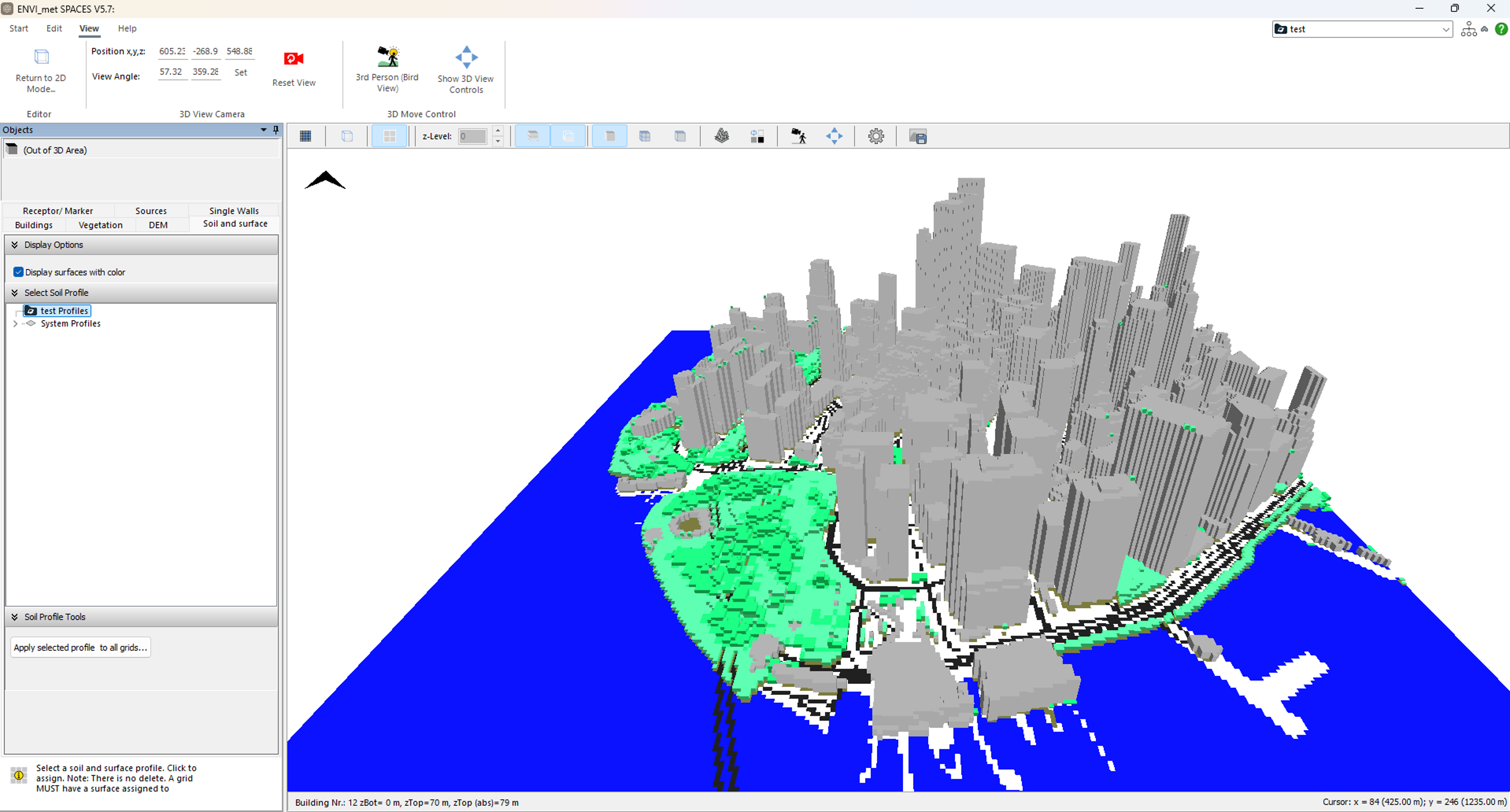
Example Output Exported in INX and Inported in ENVI-met
OBJ Files:
from voxelcity.file.obj import export_obj
output_directory = "output"
output_file_name = "voxcity"
export_obj(voxelcity_grid, output_directory, output_file_name, meshsize)
The generated OBJ files can be opened and rendered in the following 3D visualization software:
- Twinmotion: Real-time visualization tool (Free for personal use)
- Blender: Professional-grade 3D creation suite (Free)
- Rhino: Professional 3D modeling software (Commercial, offers educational licenses)
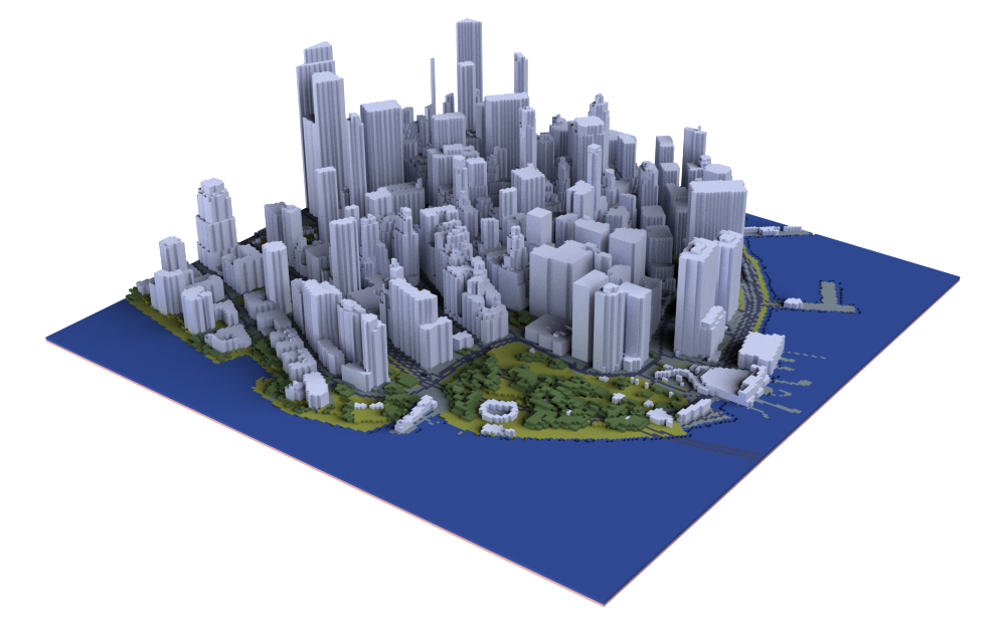

Example Output Exported in OBJ and Rendered in MagicaVoxel
MagicaVoxel VOX Files:
MagicaVoxel is a lightweight and user-friendly voxel art editor. It allows users to create, edit, and render voxel-based 3D models with an intuitive interface, making it perfect for modifying and visualizing voxelized city models. The software is free and available for Windows and Mac.
from voxelcity.file.magicavoxel import export_magicavoxel_vox
output_path = "output"
base_filename = "voxelcity"
export_magicavoxel_vox(voxelcity_grid, output_path, base_filename=base_filename)
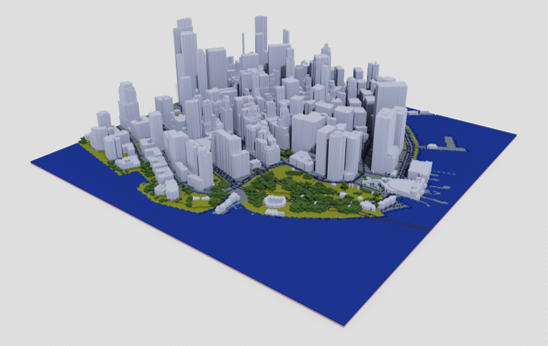
Example Output Exported in VOX and Rendered in MagicaVoxel
6. Additional Use Cases
Compute Green View Index (GVI) and Sky View Index (SVI):
from voxelcity.sim.view import get_green_view_index, get_sky_view_index
view_kwargs = {
"view_point_height": 1.5,
"dem_grid": dem_grid,
"colormap": "viridis",
"obj_export": True,
"output_directory": "output",
"output_file_name": "gvi"
}
gvi_grid = get_green_view_index(voxelcity_grid, meshsize, **view_kwargs)
view_kwargs["colormap"] = "BuPu_r"
view_kwargs["output_file_name"] = "svi"
svi_grid = get_sky_view_index(voxelcity_grid, meshsize, **view_kwargs)
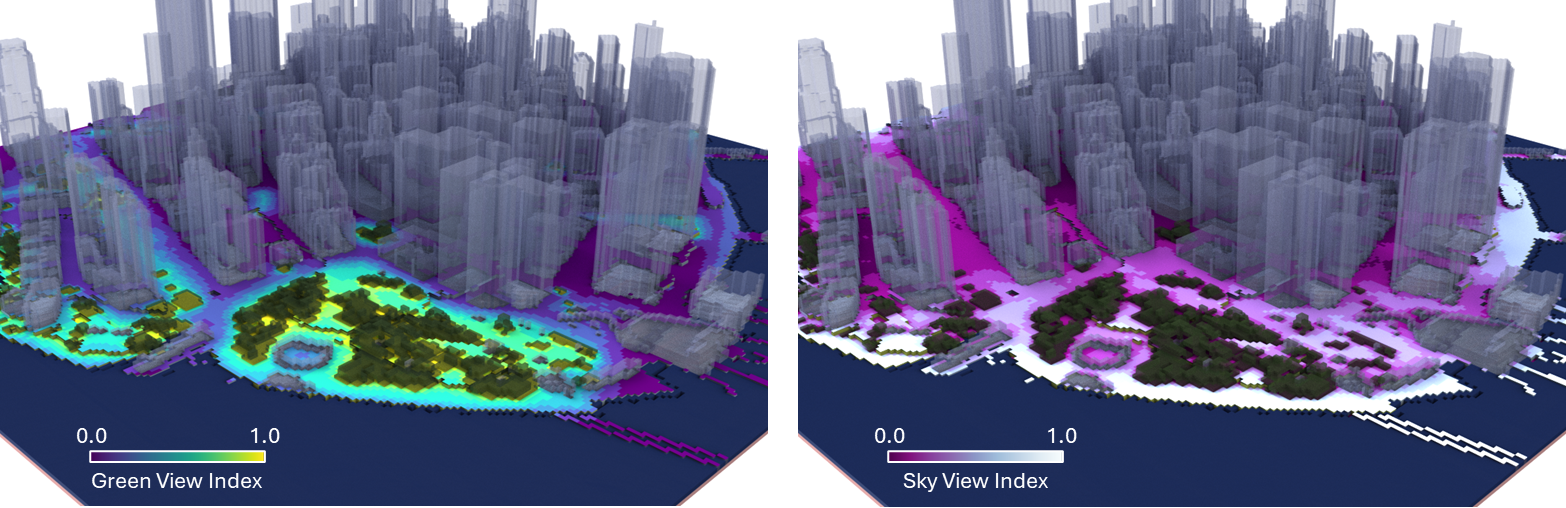
Example Results Saved as OBJ and Rendered in Rhino
Landmark Visibility Map:
from voxelcity.sim.view import get_landmark_visibility_map
landmark_kwargs = {
"view_point_height": 1.5,
"rectangle_vertices": rectangle_vertices,
"dem_grid": dem_grid,
"colormap": "cool",
"obj_export": True,
"output_directory": "output",
"output_file_name": "landmark_visibility"
}
landmark_vis_map = get_landmark_visibility_map(voxelcity_grid, building_id_grid, building_geojson, meshsize, **landmark_kwargs)
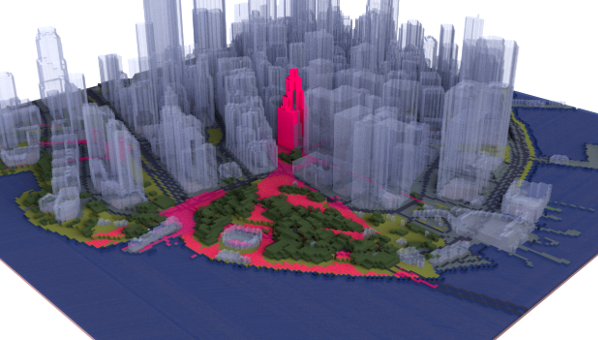
Example Result Saved as OBJ and Rendered in Rhino
References of Data Sources
Building
| Dataset | Spatial Coverage | Source/Data Acquisition |
|---|
| OpenStreetMap | Worldwide (24% completeness in city centers) | Volunteered / updated continuously |
| Global ML Building Footprints | North America, Europe, Australia | Prediction from satellite or aerial imagery / 2018-2019 for majority of the input imagery |
| Open Buildings 2.5D Temporal Dataset | Africa, Latin America, and South and Southeast Asia | Prediction from satellite imagery / 2016-2023 |
| EUBUCCO v0.1 | 27 EU countries and Switzerland (378 regions and 40,829 cities) | OpenStreetMap, government datasets / 2003-2021 (majority is after 2019) |
| UT-GLOBUS | Worldwide (more than 1200 cities or locales) | Prediction from building footprints, population, spaceborne nDSM / not provided |
| Overture Maps | Worldwide | OpenStreetMap, Esri Community Maps Program, Google Open Buildings, etc. / updated continuously |
Tree Canopy Height
Land Cover
Terrain Elevation
| Dataset | Coverage | Resolution | Source/Data Acquisition |
|---|
| FABDEM | Worldwide | 30 m | Correction of Copernicus DEM using canopy height and building footprints data / 2011-2015 (Copernicus DEM) |
| DeltaDTM | Worldwide (Only for coastal areas below 10m + mean sea level) | 30 m | Copernicus DEM, spaceborne LiDAR / 2011-2015 (Copernicus DEM) |
| USGS 3DEP 1m DEM | United States | 1 m | Aerial LiDAR / 2004-2024 (mostly after 2015) |
| England 1m Composite DTM | England | 1 m | Aerial LiDAR / 2000-2022 |
| Australian 5M DEM | Australia | 5 m | Aerial LiDAR / 2001-2015 |
| RGE Alti | France | 1 m | Aerial LiDAR |
Citation
Please cite the paper if you use voxelcity in a scientific publication:
Fujiwara, K., XXX. XXX. XXX, XXX, XXX.
@article{,
author = {Fujiwara, Kunihiko and XXX, XXX and XXX, XXX and XXX, XXX},
doi = {XXX},
journal = {XXX},
pages = {XXX},
title = {XXX},
volume = {XXX},
year = {XXX}
}
Credit
This package was created with Cookiecutter and the audreyr/cookiecutter-pypackage project template.















