PyPPL - A Python PiPeLine framework







Documentation | API | Change log
Features
- Process caching.
- Process reusability.
- Process error handling.
- Runner customization.
- Easy running profile switching.
- Plugin system.
Installation
pip install PyPPL
Plugin gallery
(*) shipped with PyPPL
Writing pipelines with predefined processes
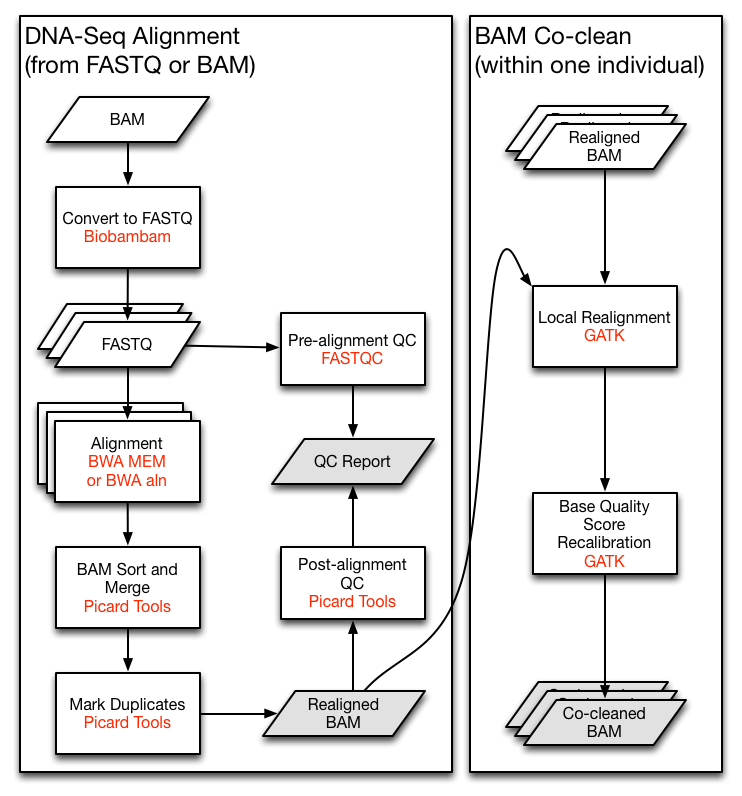
Let's say we are implementing the TCGA DNA-Seq Re-alignment Workflow
(The very left part of following figure).
For demonstration, we will skip the QC and the co-clean parts here.
demo.py:
from pyppl import PyPPL, Channel
from TCGAprocs import pBamToFastq, pAlignment, pBamSort, pBamMerge, pMarkDups
pBamToFastq.input = Channel.fromPattern('/path/to/*.bam')
pAlignment.depends = pBamToFastq
pBamSort.depends = pAlignment
pBamMerge.depends = pBamSort
pMarkDups.depends = pBamMerge
pMarkDups.config.export_dir = '/path/to/realigned_Bams'
PyPPL().start(pBamToFastq).run()

Implementing individual processes
TCGAprocs.py:
from pyppl import Proc
pBamToFastq = Proc(desc = 'Convert bam files to fastq files.')
pBamToFastq.input = 'infile:file'
pBamToFastq.output = [
'fq1:file:{{i.infile | stem}}_1.fq.gz',
'fq2:file:{{i.infile | stem}}_2.fq.gz']
pBamToFastq.script = '''
bamtofastq collate=1 exclude=QCFAIL,SECONDARY,SUPPLEMENTARY \
filename= {{i.infile}} gz=1 inputformat=bam level=5 \
outputdir= {{job.outdir}} outputperreadgroup=1 tryoq=1 \
outputperreadgroupsuffixF=_1.fq.gz \
outputperreadgroupsuffixF2=_2.fq.gz \
outputperreadgroupsuffixO=_o1.fq.gz \
outputperreadgroupsuffixO2=_o2.fq.gz \
outputperreadgroupsuffixS=_s.fq.gz
'''
pAlignment = Proc(desc = 'Align reads to reference genome.')
pAlignment.input = 'fq1:file, fq2:file'
pAlignment.output = 'bam:file:{{i.fq1 | stem | stem | [:-2]}}.bam'
pAlignment.script = '''
bwa mem -t 8 -T 0 -R <read_group> <reference> {{i.fq1}} {{i.fq2}} | \
samtools view -Shb -o {{o.bam}} -
'''
pBamSort = Proc(desc = 'Sort bam files.')
pBamSort.input = 'inbam:file'
pBamSort.output = 'outbam:file:{{i.inbam | basename}}'
pBamSort.script = '''
java -jar picard.jar SortSam CREATE_INDEX=true INPUT={{i.inbam}} \
OUTPUT={{o.outbam}} SORT_ORDER=coordinate VALIDATION_STRINGENCY=STRICT
'''
pBamMerge = Proc(desc = 'Merge bam files.')
pBamMerge.input = 'inbam:file'
pBamMerge.output = 'outbam:file:{{i.inbam | basename}}'
pBamMerge.script = '''
java -jar picard.jar MergeSamFiles ASSUME_SORTED=false CREATE_INDEX=true \
INPUT={{i.inbam}} MERGE_SEQUENCE_DICTIONARIES=false OUTPUT={{o.outbam}} \
SORT_ORDER=coordinate USE_THREADING=true VALIDATION_STRINGENCY=STRICT
'''
pMarkDups = Proc(desc = 'Mark duplicates.')
pMarkDups.input = 'inbam:file'
pMarkDups.output = 'outbam:file:{{i.inbam | basename}}'
pMarkDups.script = '''
java -jar picard.jar MarkDuplicates CREATE_INDEX=true INPUT={{i.inbam}} \
OUTPUT={{o.outbam}} VALIDATION_STRINGENCY=STRICT
'''
Each process is indenpendent so that you may also reuse the processes in other pipelines.
Pipeline flowchart
PyPPL().start(pBamToFastq).flowchart().run()
Then an SVG file endswith .pyppl.svg will be generated under current directory.
Note that this function requires Graphviz and graphviz for python.
See plugin details.

Pipeline report
See plugin details
pPyClone.report = """
## {{title}}
PyClone[1] is a tool using Probabilistic model for inferring clonal population structure from deep NGS sequencing.
}})
```table
caption: Clusters
file: "{{path.join(job.o.outdir, "tables/cluster.tsv")}}"
rows: 10
```
[1]: Roth, Andrew, et al. "PyClone: statistical inference of clonal population structure in cancer." Nature methods 11.4 (2014): 396.
"""
pPyClone.report = "file:/path/to/template.md"
PyPPL().start(pPyClone).run().report('/path/to/report', title = 'Clonality analysis using PyClone')

Full documentation
ReadTheDocs












